Page 34 - Hydrogeology Principles and Practice
P. 34
HYDC01 12/5/05 5:44 PM Page 17
Introduction 17
BO X
Continued
1. 2
terms of irrigated grain production, farming employment and rural trial wastewater discharges. These issues are interlinked but do not
poverty alleviation, together with urban and industrial water supply affect the three main hydrogeological settings equally (Table 1). A
9
3 −1
provision. An estimated water supply of 27 × 10 m a in the Hai range of water resources management strategies are considered by
river basin alone was derived from wells and boreholes in 1988 Foster et al. (2004) that could contribute to reducing and eventu-
(MWR 1992), but such large exploitation of groundwater has led to ally eliminating the current aquifer depletion and include agricul-
increasing difficulties in the last few years. tural water-saving measures, changes in land use and crop regimes,
Given the heavy dependence on groundwater resources in the artificial aquifer recharge of excess surface runoff, re-use of treated
North China Plain, a number of concerns have been identified in urban wastewater, and improved institutional arrangements that
recent years (Fig. 1) including a falling water table in the shallow deliver these water savings and technologies while at the same time
freshwater aquifer, declining water levels in the deep freshwater limiting further exploitation of groundwater for irrigated agriculture
aquifer, aquifer salinization as a result of inadequately controlled and industrial production (Foster et al. 2004).
pumping, and aquifer pollution from uncontrolled urban and indus-
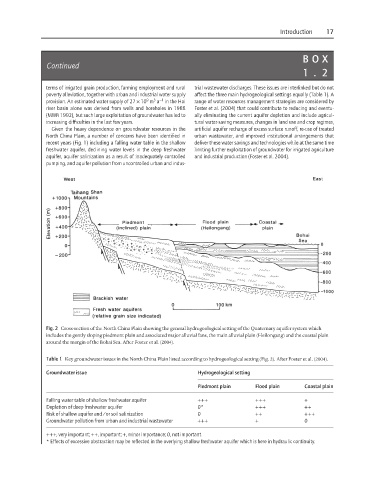
Fig. 2 Cross-section of the North China Plain showing the general hydrogeological setting of the Quaternary aquifer system which
includes the gently sloping piedmont plain and associated major alluvial fans, the main alluvial plain (Heilongang) and the coastal plain
around the margin of the Bohai Sea. After Foster et al. (2004).
Table 1 Key groundwater issues in the North China Plain listed according to hydrogeological setting (Fig. 2). After Foster et al. (2004).
Groundwater issue Hydrogeological setting
Piedmont plain Flood plain Coastal plain
Falling water table of shallow freshwater aquifer +++ +++ +
Depletion of deep freshwater aquifer 0* +++ ++
Risk of shallow aquifer and/or soil salinization 0 ++ +++
Groundwater pollution from urban and industrial wastewater +++ + 0
+++, very important; ++, important; +, minor importance; 0, not important.
* Effects of excessive abstraction may be reflected in the overlying shallow freshwater aquifer which is here in hydraulic continuity.