Page 29 - Hydrogeology Principles and Practice
P. 29
HYDC01 12/5/05 5:44 PM Page 12
12 Chapter One
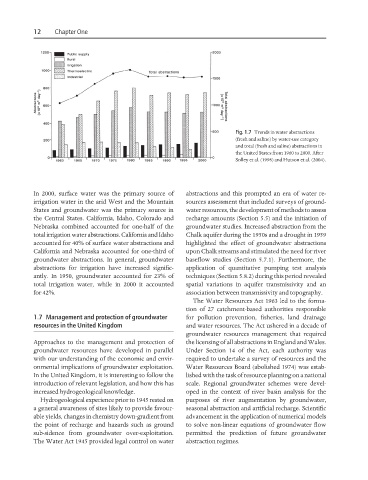
Fig. 1.7 Trends in water abstractions
(fresh and saline) by water-use category
and total (fresh and saline) abstractions in
the United States from 1960 to 2000. After
Solley et al. (1998) and Hutson et al. (2004).
In 2000, surface water was the primary source of abstractions and this prompted an era of water re-
irrigation water in the arid West and the Mountain sources assessment that included surveys of ground-
States and groundwater was the primary source in water resources, the development of methods to assess
the Central States. California, Idaho, Colorado and recharge amounts (Section 5.5) and the initiation of
Nebraska combined accounted for one-half of the groundwater studies. Increased abstraction from the
total irrigation water abstractions. California and Idaho Chalk aquifer during the 1950s and a drought in 1959
accounted for 40% of surface water abstractions and highlighted the effect of groundwater abstractions
California and Nebraska accounted for one-third of upon Chalk streams and stimulated the need for river
groundwater abstractions. In general, groundwater baseflow studies (Section 5.7.1). Furthermore, the
abstractions for irrigation have increased signific- application of quantitative pumping test analysis
antly. In 1950, groundwater accounted for 23% of techniques (Section 5.8.2) during this period revealed
total irrigation water, while in 2000 it accounted spatial variations in aquifer transmissivity and an
for 42%. association between transmissivity and topography.
The Water Resources Act 1963 led to the forma-
tion of 27 catchment-based authorities responsible
1.7 Management and protection of groundwater for pollution prevention, fisheries, land drainage
resources in the United Kingdom and water resources. The Act ushered in a decade of
groundwater resources management that required
Approaches to the management and protection of the licensing of all abstractions in England and Wales.
groundwater resources have developed in parallel Under Section 14 of the Act, each authority was
with our understanding of the economic and envir- required to undertake a survey of resources and the
onmental implications of groundwater exploitation. Water Resources Board (abolished 1974) was estab-
In the United Kingdom, it is interesting to follow the lished with the task of resource planning on a national
introduction of relevant legislation, and how this has scale. Regional groundwater schemes were devel-
increased hydrogeological knowledge. oped in the context of river basin analysis for the
Hydrogeological experience prior to 1945 rested on purposes of river augmentation by groundwater,
a general awareness of sites likely to provide favour- seasonal abstraction and artificial recharge. Scientific
able yields, changes in chemistry down-gradient from advancement in the application of numerical models
the point of recharge and hazards such as ground to solve non-linear equations of groundwater flow
sub-sidence from groundwater over-exploitation. permitted the prediction of future groundwater
The Water Act 1945 provided legal control on water abstraction regimes.