Page 29 - Illustrated Pocket Dictionary of Chromatography
P. 29
24 CAPILLARY COLUMN
¢
capacity factor, k¢ The capacity factor is a way of expressing the
retention of a compound (as a multiple of the void volume of the
system):
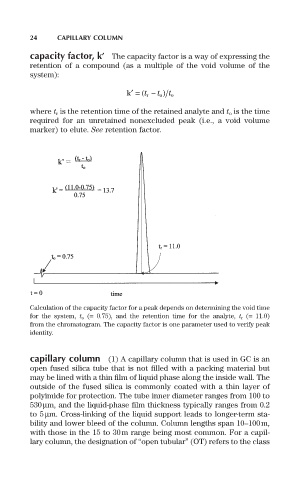
k¢= (t r - ) t o
o t
where t r is the retention time of the retained analyte and t o is the time
required for an unretained nonexcluded peak (i.e., a void volume
marker) to elute. See retention factor.
Calculation of the capacity factor for a peak depends on determining the void time
for the system, t o (= 0.75), and the retention time for the analyte, t r (= 11.0)
from the chromatogram. The capacity factor is one parameter used to verify peak
identity.
capillary column (1) A capillary column that is used in GC is an
open fused silica tube that is not filled with a packing material but
may be lined with a thin film of liquid phase along the inside wall. The
outside of the fused silica is commonly coated with a thin layer of
polyimide for protection. The tube inner diameter ranges from 100 to
530mm, and the liquid-phase film thickness typically ranges from 0.2
to 5mm. Cross-linking of the liquid support leads to longer-term sta-
bility and lower bleed of the column. Column lengths span 10–100m,
with those in the 15 to 30m range being most common. For a capil-
lary column, the designation of “open tubular” (OT) refers to the class