Page 26 - Illustrated Pocket Dictionary of Chromatography
P. 26
20 BUFFER CAPACITY (OR BUFFER INDEX), b
is holding the pH of a solution constant. In this case the buffer is com-
prised of the acid (e.g., acetic acid) and conjugate base (e.g., sodium
acetate). Conversely, a base and its conjugate acid accomplish the
same thing. The most effective buffer is obtained when the desired
-
pH is the same as the pK a of the acid (i.e., [HA] = [A ], where HA is
-
the acid and A is the conjugate base).
b
buffer capacity (or buffer index), b A quantitative means of
calculating the change of a solution pH on the addition of acid or base
to the solution. Mathematically the buffer index is written as:
dpH (for base addition or,
)
b = dC b
dpH (for acid addition )
b =-dC a
where C b and C a are the concentrations of base and acid, respectively.
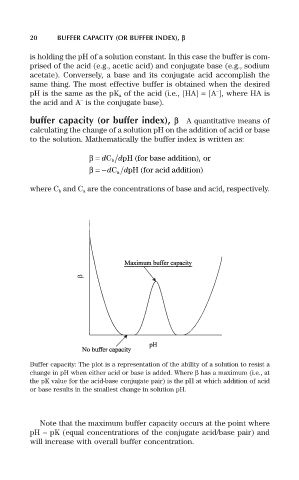
Buffer capacity: The plot is a representation of the ability of a solution to resist a
change in pH when either acid or base is added. Where b has a maximum (i.e., at
the pK value for the acid-base conjugate pair) is the pH at which addition of acid
or base results in the smallest change in solution pH.
Note that the maximum buffer capacity occurs at the point where
pH = pK (equal concentrations of the conjugate acid/base pair) and
will increase with overall buffer concentration.