Page 23 - Illustrated Pocket Dictionary of Chromatography
P. 23
BENZENE 17
Resolution is mathematically described by a resolution factor and/or
a separation factor.
beam-deflection refractive index (RI) detector Uses a split
cell: One section of the cell contains the static reference solution
(typically the mobile phase) and the other contains the flowing
mobile-phase stream. The reference solution is subtracted from the
signal of the flowing mobile, and the result is recorded as the detec-
tor output. The beam-deflection RI is useful over the entire refractive
index range (unlike the Fresnel RI).
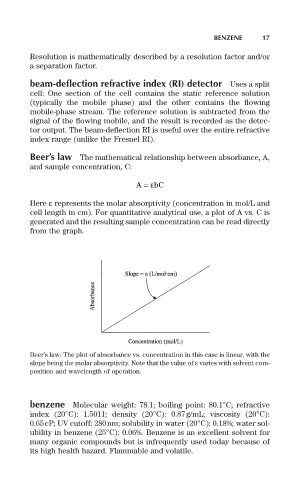
Beer’s law The mathematical relationship between absorbance, A,
and sample concentration, C:
A =e bC
Here e represents the molar absorptivity (concentration in mol/L and
cell length in cm). For quantitative analytical use, a plot of A vs. C is
generated and the resulting sample concentration can be read directly
from the graph.
Beer’s law: The plot of absorbance vs. concentration in this case is linear, with the
slope being the molar absorptivity. Note that the value of e varies with solvent com-
position and wavelength of operation.
benzene Molecular weight: 78.1; boiling point: 80.1°C; refractive
index (20°C): 1.5011; density (20°C): 0.87g/mL; viscosity (20°C):
0.65cP; UV cutoff: 280nm; solubility in water (20°C): 0.18%; water sol-
ubility in benzene (25°C): 0.06%. Benzene is an excellent solvent for
many organic compounds but is infrequently used today because of
its high health hazard. Flammable and volatile.