Page 141 - Improving Machinery Reliability
P. 141
Machinery Reliability Audits and Reviews 113
Transient Torsional Analysis
After the steady state analysis is made, a transient analysis should be made to
evaluate the startup stresses and allowable number of startups for synchronous motor
systems.22,26 The transient analysis refers to the conditions on startup, which are con-
tinually changing because of the increasing torque and speed of the system. When a
synchronous motor starts, an excitation is imposed upon the torsional system due to
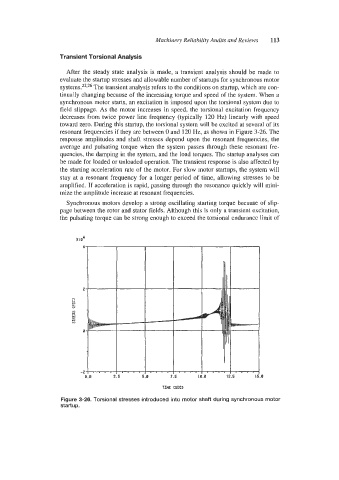
field slippage. As the motor increases in speed, the torsional excitation frequency
decreases from twice power line frequency (typically 120 Hz) linearly with speed
toward zero. During this startup, the torsional system will be excited at several of its
resonant frequencies if they are between 0 and 120 Hz, as shown in Figure 3-26. The
response amplitudes and shaft stresses depend upon the resonant frequencies, the
average and pulsating torque when the system passes through these resonant fre-
quencies, the damping in the system, and the load torques. The startup analyses can
be made for loaded or unloaded operation. The transient response is also affected by
the starting acceleration rate of the motor. For slow motor startups, the system will
stay at a resonant frequency for a longer period of time, allowing stresses to be
amplified. If acceleration is rapid, passing through the resonance quickly will mini-
mize the amplitude increase at resonant frequencies.
Synchronous motors develop a strong oscillating starting torque because of slip-
page between the rotor and stator fields. Although this is only a transient excitation,
the pulsating torque can be strong enough to exceed the torsional endurance limit of
Figure 3-26. Torsional stresses introduced into motor shaft during synchronous motor
startup.