Page 207 - Industrial Cutting of Textile Materials
P. 207
194 Industrial Cutting of Textile Materials
12
9
10
11
States), Hashima (Japan), Oshima (Taiwan), Fiblon (South Korea), Weishi
(China), and others.
12.3.1 The discontinuous work process (flat, scissor type)
fusing press
The discontinuous work process fusing press has a heating zone with two work sur-
faces. Depending upon the construction, there are two ways in which the work surfaces
may move to open the press: an upper surface that folds sideways (fusing plate press)
and an upper or lower surface that is moved whilst maintaining its parallel position.
12.3.1.1 Press with a side-folding surface
These are simple and less powerful presses, designed for occasional use in the produc-
tion process, and consist of the following:
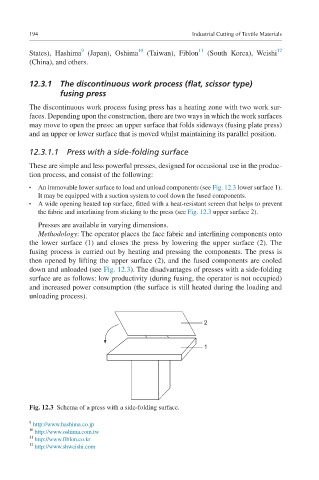
An immovable lower surface to load and unload components (see Fig. 12.3 lower surface 1).
●
It may be equipped with a suction system to cool down the fused components.
A wide opening heated top surface, fitted with a heat-resistant screen that helps to prevent
●
the fabric and interlining from sticking to the press (see Fig. 12.3 upper surface 2).
Presses are available in varying dimensions.
Methodology: The operator places the face fabric and interlining components onto
the lower surface (1) and closes the press by lowering the upper surface (2). The
fusing process is carried out by heating and pressing the components. The press is
then opened by lifting the upper surface (2), and the fused components are cooled
down and unloaded (see Fig. 12.3). The disadvantages of presses with a side-folding
surface are as follows: low productivity (during fusing, the operator is not occupied)
and increased power consumption (the surface is still heated during the loading and
unloading process).
2
1
Fig. 12.3 Schema of a press with a side-folding surface.
9 http://www.hashima.co.jp
10 http://www.oshima.com.tw
11 http://www.fiblon.co.kr
12 http://www.shweishi.com