Page 297 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 297
12/276 Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
installations that contain high harmonics and that may influence its life. For higher unbalances, a derating of the
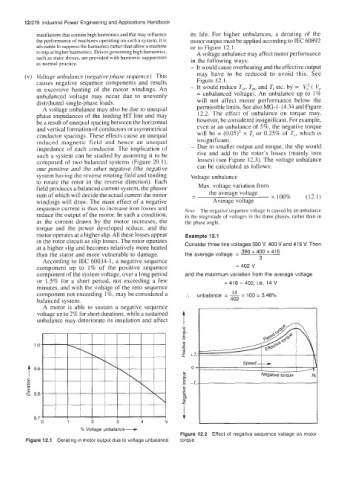
the performance of machines operating on such a system, it is motor output must be applied according to IEC 60892
advisable to suppress the harmonics rather than allow a machine or to Figure 12.1.
to trip at higher harmonics. Drives generating high harmonics, A voltage unbalance may affect motor performance
such as static drives, are provided with harmonic suppressors in the following ways:
as normal practice.
- It would cause overheating and the effective output
(v) Voltage unbalance (negative phase sequence) This mav have to be reduced to avoid this. See
causes negative sequence components and results Figure 12.1.
in excessive heating of the motor windings. An - It would reduce T,,, T,,, and T, etc. by 0~ Vu2 ( Vu
unbalanced voltage may occur due to unevenly = unbalanced voltagd. An unbalance up to 1%
distributed single-phase loads. will not affect motor performance below the
A voltage unbalance may also be due to unequal permissible limits. See also MG-1-14.34 and Figure
phase impedances of the feeding HT line and may 12.2. The effect of unbalance on torque may,
be a result of unequal spacing between the horizontal however, be considered insignificant. For example,
and vertical formation of conductors or asymmetrical even at an unbalance of 5%, the negative torque
conductor spacings. These effects cause an unequal will be = (0.05)* x T, or 0.25% of Tr, which is
induced magnetic field and hence an unequal insignificant.
impedance of each conductor. The implication of - Due to smaller output and torque, the slip would
such a system can be studied by assuming it to be rise and add to the rotor's losses (mainly iron
composed of two balanced systems (Figure 20.1), losses) (see Figure 12.3). The voltage unbalance
one positive and the other negative (the negative can be calculated as follows:
system having the reverse rotating field and tending Voltage unbalance
to rotate the rotor in the reverse direction). Each
field produces a balanced current system, the phasor Max. voltage variation from
sum of which will decide the actual current the motor - the average voltage x 100% (12.1)
-
windings will draw. The main effect of a negative Average voltage
sequence current is thus to increase iron losses and Norr The negative sequence voltage is caused by an unbalance
reduce the output of the motor. In such a condition, in the magnitude of voltages in the three phases, rather than in
as the current drawn by the motor increases, the the phase angle.
torque and the power developed reduce, and the
motor operates at a higher slip. All these losses appear Example 12.1
in the rotor circuit as slip losses. The rotor operates
at a higher slip and becomes relatively more heated Consider three line voltages 390 V, 400 V and 41 6 V. Then
than the stator and more vulnerable to damage. the average voltage = 390+400+416
According to IEC 60034- 1, a negative sequence 3
component up to 1% of the positive sequence = 402 V
component of the system voltage, over a long period and the maximum variation from the average voltage
or 1.5% for a short period, not exceeding a few = 416 - 402, Le. 14 V
minutes, and with the voltage of the zero sequence
component not exceeding 1 %, may be considered a :. unbalance = 14 100 = 3.48%
x
balanced system. 402
A motor is able to sustain a negative sequence
voltage up to 2% for short durations, while a sustained
unbalance may deteriorate its insulation and affect
1
to m
C e Negative torque
.- P -Tr
c
E
Q O
% Voltage unbalance -
0.I I
0 1 2 3 4 5
Figure 12.2 Effect of negative sequence voltage on motor
Figure 12.1 Derating in motor output due to voltage unbalance torque