Page 40 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 40
Theory, performance and constructional features of induction motors 1/21
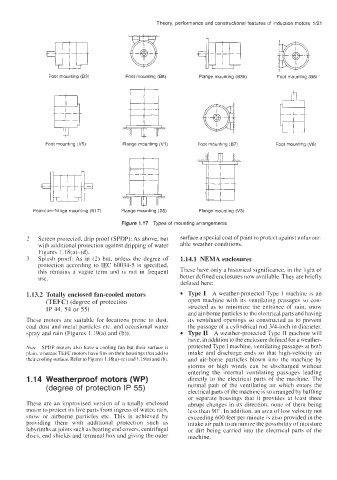
Foot mounting (83) Foot mounting (88) Flange mounting (835) Foot mounting (86)
Foot mounting (V5) Flange mounting (VI) Foot mounting (87) Foot mounting (V6)
.
. - -. -
.
Foot-cum-flange mounting (817) Flange mounting (85) Flange mounting (V3)
Figure 1.17 Types of mounting arrangements
2 Screen protected, drip proof (SPDP): As above, but surface a special coat of paint to protcct against unfavour-
with additional protection against dripping of water able weather conditions.
Figures 1. I8(a)-(d).
3 Splash proof: As in (2) but, unless the degree of 1.14.1 NEMA enclosures
protection according to IEC 60034-5 is specified,
this remains a vague term and is not in frequent These have only a historical significance, in the light of
use. better defined enclosures now available. They are briefly
defined here:
1.13.2 Totally enclosed fan-cooled motors Type I A weather-protected Type I machine is an
(TEFC) (degree of protection open machine with its ventilating passages so con-
1P 44, 54 or 55) structed as to minimize the entrance of rain, snow
and air-borne particles to the electrical parts and having
These motors are suitable for locations prone to dust, its ventilated openings so constructed as to prevent
coal dust and metal particles etc. and occasional water the passage of a cylindrical rod 3/4-inch in diameter.
spray and rain (Figures 1.19(a) and (b)). Type I1 A weather-protected Type I1 machine will
have, in addition to the enclosure defined for a weather-
Nofr SPDP motors also have a cooling fan but their surface is protected Type 1 machine, ventilating passages at both
plain. whereas TEFC motors have fins on their housings that add to intake and discharge ends so that high-velocity air
their cooling surface. Refer to Figures 1.18(at(c) and 1.19(a) and (b). and air-borne particles blown into the machine by
storms or high winds can be discharged without
entering the internal ventilating passages leading
1 .I 4 Weatherproof motors (WP) directly to the electrical parts of the machine. The
(degree of protection IP 55) normal path of the ventilating air which enters the
electrical parts of the machine is so arranged by baffling
or separate housings that it provides at least three
These are an improvised version of a totally enclosed abrupt changes in its direction, none of them being
motor to protect its live parts from ingress of water, rain, less than 90". In addition. an area of low velocity not
snow or airborne particles etc. This is achieved by exceeding 600 feet per minute is also provided in the
providing them with additional protection such as intake air path to minimize the possibility of moisture
labyrinths at joints such as bearing end covers, centrifugal or dirt being carried into the electrical parts of the
discs, end shields and terminal box and giving the outer machine.