Page 666 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 666
Circuit interrupters 191631
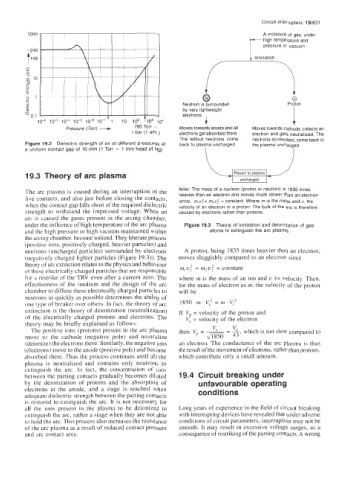
1000 , A molecule of gas, undei
-high temperature and
pressure or vacuum.
t
1240
A
by very lightweight I
electronS 4
1-1 ' 1
Pressure (Torr) -+ 760 Torr = Moves towards anode and all Moves towards cathode, collects an
1 bar (1 atm.) electrons get absorbed there. electron and gets neutralized. The
The leftout neutrons come neutrons so resulted, come back to
Figure 19.2 Dielectric strength of air at different pressures at back to plasma uncharged the plasma uncharged
a uniform contact gap of 10 mm (1 Torr = 1 mm head of Hg)
19.3 Theory of arc plasma
Note: The mass of a nucleon (proton or neutron) IS 1835 times
The arc plasma is caused during an interruption of the heavier than an electron and moves much slower than an electron
live contacts, and also just before closing the contacts, since, m,v: = rn,v: = constant. Where rn IS the mass and v, the
when the contact gap falls short of the required dielectric velocity of an electron or a proton. The bulk of the arc is therefore
strength to withstand the impressed voltage. When an caused by electrons rather than protons.
arc is caused the gases present in the arcing chamber,
under the influence of high temperature of the arc plasma Figure 19.3 Theory of ionization and deionization of gas
and the high pressure or high vacuum maintained within atoms to extinguish the arc plasma
the arcing chamber, become ionized. They liberate protons
(positive ions, positively charged, heavier particles) and
neutrons (uncharged particles) surrounded by electrons A proton, being 183.5 times heavier than an electron,
(negatively charged lighter particles (Figure 19.3)). The moves sluggishly compared to an electron since
theory of arc extinction relates to the physics and behaviour m,uf = rn2ui = constant
of these electrically charged particles that are responsible
for a restrike of the TRV even after a current zero. The where m is the mass of an ion and u its velocity. Then,
effectiveness of the medium and the design of the arc for the mass of electron as rn, the velocity of the proton
chamber to diffuse these electrically charged particles to will be
neutrons as quickly as possible determines the ability of
one type of breaker over others. In fact, the theory of arc
extinction is the theory of deionization (neutralization) If Vp = velocity of the proton and
of the electrically charged protons and electrons. The V, = velocity of the electron
theory may be briefly explained as follows.
The positive ions (protons) present in the arc plasma - - which is too slow compared to
then Vp = ~
move to the cathode (negative pole) and neutralize @mi - 43'
(deionize) the electrons there. Similarly, the negative ions an electron. The conductance of the arc plasma is thus
(electrons) move to the anode (positive pole) and become the result of the movement of electrons, rather than protons.
absorbed there. Thus the process continues until all the which contribute only a small amount.
plasma is neutralized and contains only neutrons to
extinguish the arc. In fact, the concentration of ions
between the parting contacts gradually becomes diluted 19.4 Circuit breaking under
by the deionization of protons and the absorption of u nfavoura ble operating
electrons at the anode, and a stage is reached when conditions
adequate dielectric strength between the parting contacts
is restored to extinguish the arc. It is not necessary for
all the ions present in the plasma to be deionized to Long years of experience in the field of circuit breaking
extinguish the arc, rather a stage when they are not able with interrupting devices have revealed that under adverse
to hold the arc. This process also increases the resistance conditions of circuit parameters, interruption may not be
of the arc plasma as a result of reduced contact pressure smooth. It may result in excessive voltage surges, as a
and arc contact area. consequence of restriking of the parting contacts. A wrong