Page 188 - Industrial Ventilation Design Guidebook
P. 188
i 50 CHAPTER 4 PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS
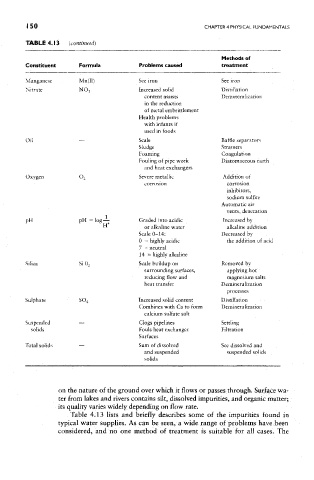
TABLE 4.13 (continued]
Methods of
Constituent Formula Problems caused treatment
Manganese Mn(II) See iron See iron
Nitrate NO 3 Increased solid Distillation
content assists Demineralization
in the reduction
of metal embrittlement
Health problems
with infants if
used in foods
Oil Scale Baffle separators
Sludge Strainers
Foaming Coagulation
Fouling of pipe work Diatomaceous earth
and heat exchangers
Oxygen O? Severe metallic Addition of
corrosion corrosion
inhibitors,
sodium sulfite
Automatic air
vents, deaeration
pH pH = log— - Graded into acidic Increased by
H or alkaline water alkaline addition
Scale 0-14: Decreased by
0 = highly acidic the addition of acid
7 = neutral
14 = highly alkaline
Silica Si 0 2 Scale buildup on Removed by
surrounding surfaces, applying hot
reducing flow and magnesium salts
heat transfer Demineralization
processes
Sulphate SO 4 Increased solid content Distillation
Combines with Ca to form Demineralization
calcium sulfate salt
Suspended — Clogs pipelines Settling
solids Fouls heat exchanger Filtration
Surfaces
Total solids — Sum of dissolved See dissolved and
and suspended suspended solids
solids
on the nature of the ground over which it flows or passes through. Surface wa-
ter from lakes and rivers contains silt, dissolved impurities, and organic matter;
its quality varies widely depending on flow rate.
Table 4.13 lists and briefly describes some of the impurities found in
typical water supplies. As can be seen, a wide range of problems have been
considered, and no one method of treatment is suitable for all cases. The