Page 328 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 328
maintenance
higher
for
(common
and
and
7)
efficiency
&
costs
cost
6
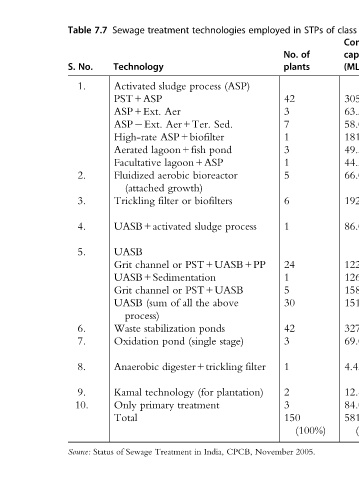
S.No.
Higher
issue
land
Poor
7.8
31.6
23.0
4.5
50.5
0.1
1.2
2.7
26.0
5.6
5812.83
1513.90
327.53
158.17
69.00
4.45
class cities I Average Combined size Age % capacity Remarks (MLD) capacity (MLD) for preference The 72.8 52.6 3059.63 is ASP conventional 21.1 1.1 63.36 more in realized 8.3 1.0 58.04 others the than installations 181.8 3.1 181.84 16.5 0.9 49.50 44.5 0.8 44.50 to due objection Obvious 13.2 1.1
of
STPs of (100%) 2005.
in No. plants 42 3 7 1 3 1 5 6 1 24 1 5 30 42 3 1 2 3 150
employed filter November
technologies (ASP) process Sed. pond lagoon+ASP bioreactor biofilters process sludge PST+UASB+PP PST+UASB above the ponds stage) (single digester+trickling plantation) (for treatment CPCB, India, in
treatment sludge Aer Aer+Ter. ASP+biofilter lagoon+fish aerobic growth) or filter UASB+activated or channel UASB+Sedimentation or channel all of (sum stabilization pond technology primary Treatment
Sewage Technology Activated PST+ASP ASP+Ext. ASP Ext. High-rate Aerated Facultative Fluidized (attached Trickling UASB Grit Grit UASB process) Waste Oxidation Anaerobic Kamal Only Total Sewage of
7.7 Status
Table No. S. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Source: