Page 338 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 338
310 Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling, and Reuse
wastewater is reported to be extremely complex in nature, consisting of
municipal sewage, which is mixed with pollutants of various industrial
wastes. The main objective of the recycling and reuse of sewage is for various
nonpotable industrial uses. Municipal sewage generated in the vicinity of the
Rashtriya Chemicals and Fertilizers (RCF) Plant, Chembur, Mumbai, is
heavily contaminated with various streams of industrial wastes and results
in complex wastewater. In order to become water self-sufficient and to meet
increasing process water requirements, the RCF Plant realizes the impor-
tance of recycling and reuse of wastewater for nonpotable industrial use
and commissioned a sewage reclamation plant for the industry
(MoEF, 2011).
7.4.1.1 Salient Features
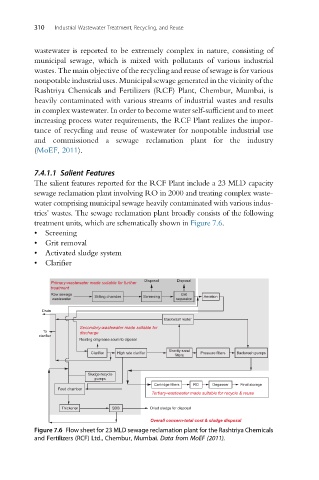
The salient features reported for the RCF Plant include a 23 MLD capacity
sewage reclamation plant involving RO in 2000 and treating complex waste-
water comprising municipal sewage heavily contaminated with various indus-
tries’ wastes. The sewage reclamation plant broadly consists of the following
treatment units, which are schematically shown in Figure 7.6.
• Screening
• Grit removal
• Activated sludge system
• Clarifier
Primary-wastewater made suitable for further Disposal Disposal
treatment
Raw sewage Stilling chamber Screening Grit Aeration
wastewater separator
Drain
Backwash water
Secondary-wastewater made suitable for
To discharge
clarifier
Floating oil/grease scum to diposal
Gravity sand
Clarifier High rate clarifier Pressure filters Backwash pumps
filters
Sludge recycle
pumps
Cartridge filters RO Degasser Final storage
Feed chamber
Tertiary-wastewater made suitable for recycle & reuse
Thickener SDB Dried sludge for disposal
Overall concern-total cost & sludge disposal
Figure 7.6 Flow sheet for 23 MLD sewage reclamation plant for the Rashtriya Chemicals
and Fertilizers (RCF) Ltd., Chembur, Mumbai. Data from MoEF (2011).