Page 379 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 379
Phenolic Wastewater Treatment: Development and Applications of New Adsorbent Materials 351
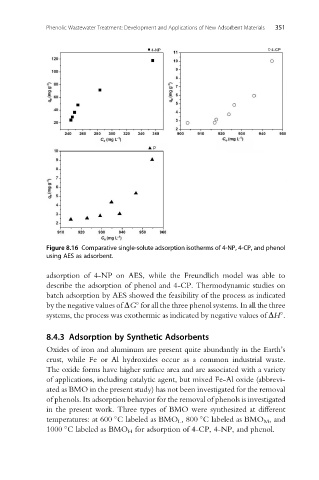
Figure 8.16 Comparative single-solute adsorption isotherms of 4-NP, 4-CP, and phenol
using AES as adsorbent.
adsorption of 4-NP on AES, while the Freundlich model was able to
describe the adsorption of phenol and 4-CP. Thermodynamic studies on
batch adsorption by AES showed the feasibility of the process as indicated
by the negative values of DG for all the three phenol systems. In all the three
systems, the process was exothermic as indicated by negative values of DH .
8.4.3 Adsorption by Synthetic Adsorbents
Oxides of iron and aluminum are present quite abundantly in the Earth’s
crust, while Fe or Al hydroxides occur as a common industrial waste.
The oxide forms have higher surface area and are associated with a variety
of applications, including catalytic agent, but mixed Fe-Al oxide (abbrevi-
ated as BMO in the present study) has not been investigated for the removal
of phenols. Its adsorption behavior for the removal of phenols is investigated
in the present work. Three types of BMO were synthesized at different
temperatures: at 600 C labeled as BMO L , 800 C labeled as BMO M , and
1000 C labeled as BMO H for adsorption of 4-CP, 4-NP, and phenol.