Page 376 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 376
348 Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling, and Reuse
8.4.1.1 Untreated Banana Peel
Earlier researchers have utilized banana pith (Namasivayam and Kanchana,
1992) for the removal of colors from wastewater, but the peel of the fruit
itself has not been utilized for the removal of phenolic compounds. BP
was collected from the local market in the Silchar area of northeast India
in large batches as required.
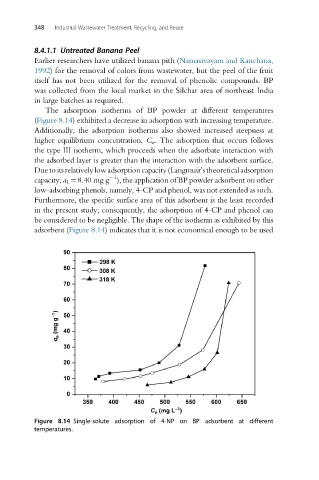
The adsorption isotherms of BP powder at different temperatures
(Figure 8.14) exhibited a decrease in adsorption with increasing temperature.
Additionally, the adsorption isotherms also showed increased steepness at
higher equilibrium concentration, C e . The adsorption that occurs follows
the type III isotherm, which proceeds when the adsorbate interaction with
the adsorbed layer is greater than the interaction with the adsorbent surface.
Duetoitsrelativelylowadsorptioncapacity(Langmuir’stheoreticaladsorption
1
capacity, a L ¼8.40 mg g ), the application of BP powder adsorbent on other
low-adsorbing phenols, namely, 4-CP and phenol, was not extended as such.
Furthermore, the specific surface area of this adsorbent is the least recorded
in the present study; consequently, the adsorption of 4-CP and phenol can
be considered to be negligible. The shape of the isotherm as exhibited by this
adsorbent (Figure 8.14) indicates that it is not economical enough to be used
Figure 8.14 Single-solute adsorption of 4-NP on BP adsorbent at different
temperatures.