Page 437 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 437
Application of Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor 409
Number of articles published in peer-reviewed journals
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010
Year
UASB AnMBR
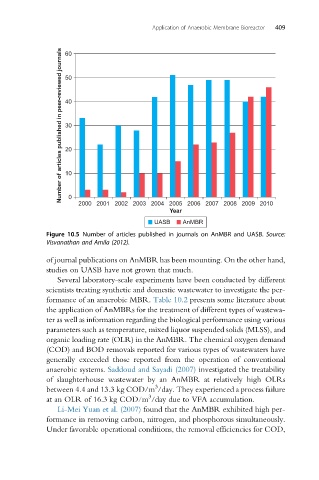
Figure 10.5 Number of articles published in journals on AnMBR and UASB. Source:
Visvanathan and Amila (2012).
of journal publications on AnMBR has been mounting. On the other hand,
studies on UASB have not grown that much.
Several laboratory-scale experiments have been conducted by different
scientists treating synthetic and domestic wastewater to investigate the per-
formance of an anaerobic MBR. Table 10.2 presents some literature about
the application of AnMBRs for the treatment of different types of wastewa-
ter as well as information regarding the biological performance using various
parameters such as temperature, mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSS), and
organic loading rate (OLR) in the AnMBR. The chemical oxygen demand
(COD) and BOD removals reported for various types of wastewaters have
generally exceeded those reported from the operation of conventional
anaerobic systems. Saddoud and Sayadi (2007) investigated the treatability
of slaughterhouse wastewater by an AnMBR at relatively high OLRs
3
between 4.4 and 13.3 kg COD/m /day. They experienced a process failure
3
at an OLR of 16.3 kg COD/m /day due to VFA accumulation.
Li-Mei Yuan et al. (2007) found that the AnMBR exhibited high per-
formance in removing carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorous simultaneously.
Under favorable operational conditions, the removal efficiencies for COD,