Page 512 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 512
482 Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling, and Reuse
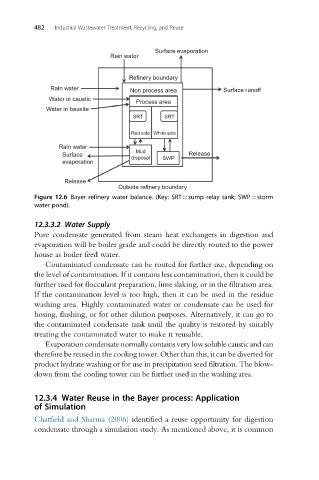
Surface evaporation
Rain water
Refinery boundary
Rain water Non process area Surface runoff
Water in caustic
Process area
Water in bauxite
SRT SRT
Red side White side
Rain water
Mud
Surface Release
disposal SWP
evaporation
Release
Outside refinery boundary
Figure 12.6 Bayer refinery water balance. (Key: SRT¼sump relay tank; SWP¼storm
water pond).
12.3.3.2 Water Supply
Pure condensate generated from steam heat exchangers in digestion and
evaporation will be boiler grade and could be directly routed to the power
house as boiler feed water.
Contaminated condensate can be routed for further use, depending on
the level of contamination. If it contains less contamination, then it could be
further used for flocculant preparation, lime slaking, or in the filtration area.
If the contamination level is too high, then it can be used in the residue
washing area. Highly contaminated water or condensate can be used for
hosing, flushing, or for other dilution purposes. Alternatively, it can go to
the contaminated condensate tank until the quality is restored by suitably
treating the contaminated water to make it reusable.
Evaporation condensate normally containsverylowsoluble caustic and can
therefore be reused in the cooling tower. Other than this, it can be diverted for
product hydrate washing or for use in precipitation seed filtration. The blow-
down from the cooling tower can be further used in the washing area.
12.3.4 Water Reuse in the Bayer process: Application
of Simulation
Chatfield and Sharma (2006) identified a reuse opportunity for digestion
condensate through a simulation study. As mentioned above, it is common