Page 136 - Innovations in Intelligent Machines
P. 136
Evolution-based Dynamic Path Planning for Autonomous Vehicles 127
G
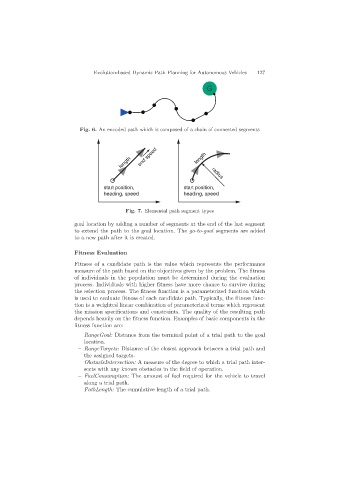
Fig. 6. An encoded path which is composed of a chain of connected segments
length end speed length radius
start position, start position,
heading, speed heading, speed
Fig. 7. Elemental path segment types
goal location by adding a number of segments at the end of the last segment
to extend the path to the goal location. The go-to-goal segments are added
to a new path after it is created.
Fitness Evaluation
Fitness of a candidate path is the value which represents the performance
measure of the path based on the objectives given by the problem. The fitness
of individuals in the population must be determined during the evaluation
process. Individuals with higher fitness have more chance to survive during
the selection process. The fitness function is a parameterized function which
is used to evaluate fitness of each candidate path. Typically, the fitness func-
tion is a weighted linear combination of parameterized terms which represent
the mission specifications and constraints. The quality of the resulting path
depends heavily on the fitness function. Examples of basic components in the
fitness function are:
– RangeGoal: Distance from the terminal point of a trial path to the goal
location.
– RangeTargets: Distance of the closest approach between a trial path and
the assigned targets.
– ObstacleIntersection: A measure of the degree to which a trial path inter-
sects with any known obstacles in the field of operation.
– FuelConsumption: The amount of fuel required for the vehicle to travel
along a trial path.
– PathLength: The cumulative length of a trial path.