Page 138 - Innovations in Intelligent Machines
P. 138
Evolution-based Dynamic Path Planning for Autonomous Vehicles 129
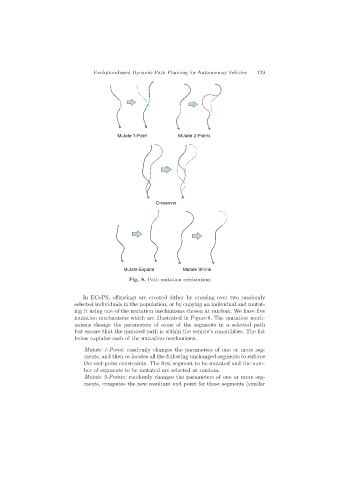
Mutate 1-Point Mutate 2-Points
Crossover
Mutate Expand Mutate Shrink
Fig. 8. Path mutation mechanisms
In ECoPS, offsprings are created either by crossing over two randomly
selected individuals in the population, or by copying an individual and mutat-
ing it using one of the mutation mechanisms chosen at random. We have five
mutation mechanisms which are illustrated in Figure 8. The mutation mech-
anisms change the parameters of some of the segments in a selected path
but ensure that the mutated path is within the vehicle’s capabilities. The list
below explains each of the mutation mechanisms.
– Mutate 1-Point: randomly changes the parameters of one or more seg-
ments, and then re-locates all the following unchanged segments to enforce
the end-point constraints. The first segment to be mutated and the num-
ber of segments to be mutated are selected at random.
– Mutate 2-Points: randomly changes the parameters of one or more seg-
ments, computes the new resultant end point for those segments (similar