Page 270 - Innovations in Intelligent Machines
P. 270
Toward Robot Perception through Omnidirectional Vision 263
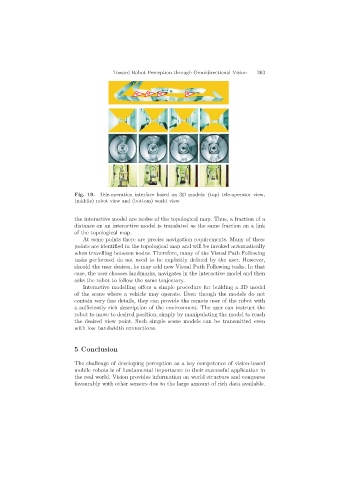
Fig. 19. Tele-operation interface based on 3D models: (top) tele-operator view,
(middle) robot view and (bottom) world view
the interactive model are nodes of the topological map. Thus, a fraction of a
distance on an interactive model is translated as the same fraction on a link
of the topological map.
At some points there are precise navigation requirements. Many of these
points are identified in the topological map and will be invoked automatically
when travelling between nodes. Therefore, many of the Visual Path Following
tasks performed do not need to be explicitly defined by the user. However,
should the user desires, he may add new Visual Path Following tasks. In that
case, the user chooses landmarks, navigates in the interactive model and then
asks the robot to follow the same trajectory.
Interactive modelling offers a simple procedure for building a 3D model
of the scene where a vehicle may operate. Even though the models do not
contain very fine details, they can provide the remote user of the robot with
a sufficiently rich description of the environment. The user can instruct the
robot to move to desired position, simply by manipulating the model to reach
the desired view point. Such simple scene models can be transmitted even
with low bandwidth connections.
5 Conclusion
The challenge of developing perception as a key competence of vision-based
mobile robots is of fundamental importance to their successful application in
the real world. Vision provides information on world structure and compares
favourably with other sensors due to the large amount of rich data available.