Page 83 - Innovations in Intelligent Machines
P. 83
72 P.B. Sujit et al.
x 10 4 q = 1 5 x 10 4 q = 2
5
4.5 4 4.5 4
Total uncertainty 3.5 3 Cooperative Total uncertainty 3.5 3 Greedy
2.5
2 Greedy 2.5 Cooperative
Nash 2
Coalition Nash Nash
1.5 Coalition Nash
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 1.5
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200
Number of steps Number of steps
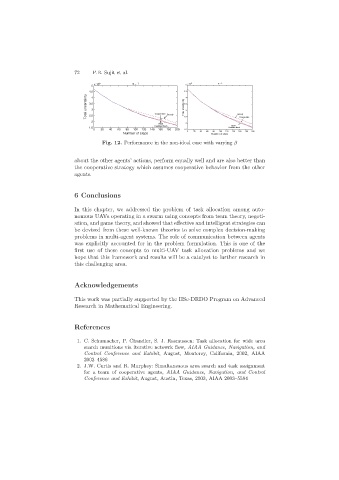
Fig. 12. Performance in the non-ideal case with varying β
about the other agents’ actions, perform equally well and are also better than
the cooperative strategy which assumes cooperative behavior from the other
agents.
6 Conclusions
In this chapter, we addressed the problem of task allocation among auto-
nomous UAVs operating in a swarm using concepts from team theory, negoti-
ation, and game theory, and showed that effective and intelligent strategies can
be devised from these well-known theories to solve complex decision-making
problems in multi-agent systems. The role of communication between agents
was explicitly accounted for in the problem formulation. This is one of the
first use of these concepts to multi-UAV task allocation problems and we
hope that this framework and results will be a catalyst to further research in
this challenging area.
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the IISc-DRDO Program on Advanced
Research in Mathematical Engineering.
References
1. C. Schumacher, P. Chandler, S. J. Rasmussen: Task allocation for wide area
search munitions via iterative netowrk flow, AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and
Control Conference and Exhibit, August, Monterey, California, 2002, AIAA
2002–4586
2. J.W. Curtis and R. Murphey: Simultaneaous area search and task assignment
for a team of cooperative agents, AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control
Conference and Exhibit, August, Austin, Texas, 2003, AIAA 2003–5584