Page 177 - Inorganic Mass Spectrometry - Fundamentals and Applications
P. 177
Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry 16.5
S LIT
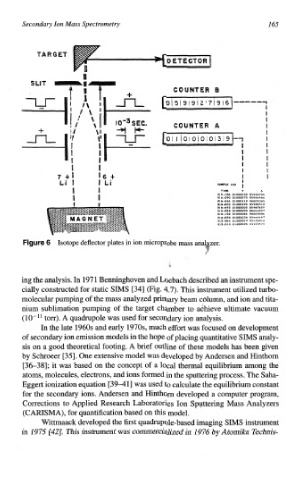
Figure 6 Isotope deflector plates in ion microprobe mass aJi
ing the analysis. In 197 l Benninghoven and Loebach described an ins~ment spe-
cially constructed for static SIMS [34] (Fig. 4.7). This ins~ment utilized turbo-
molecular pumping of the mass analyzed primary beam cdlumn, and ion and tita-
nium sublimation pumping of the target chamber to hieve ultimate vacuum
( torr). A quadrupole was used for secondary ion analysis.
In the late 1960s and early 1970s, much effort was focused on development
of secondary ion emission models in the hope of placing quantitative SIMS analy-
sis on a good theoretical footing. A brief outline of these models has been given
by Schroeer [35]. One extensive model was developed by Andersen and Hinthorn
[36"38]; it was based on the concept of a local thermal equilibrium among the
atoms, molecules, electrons, and ions formed in the sputtering process. The Saha-
Eggert ionization equation E39411 was used to calculate the equilibrium constant
for the secondary ions. Andersen and Hinthorn developed a computer program,
Corrections to Applied Research Laboratories Ion Sputtering Mass Analyzers
(CARISMA), for quantification based on this model.
Wittmaack developed the first quadrupole-based imaging SIMS ins~ment
in 1975 [42]. This ins~ment was commercialized in 1976 by Atornika Technis-