Page 178 - Inorganic Mass Spectrometry - Fundamentals and Applications
P. 178
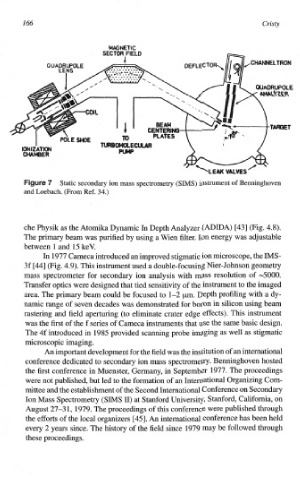
166 Cristy
and Loebach. (From Ref, 34.)
che Physik as the Atomika Dynamic In Depth Analyzer (ADDA) [43] (Fig. 4.8).
The primary beam was purified by using a Wien filter. Ion energy was adjustable
between l and 15 keV.
In 1977 Cameca introduced an improved stigmatic ion microscope, the
MS-
3f E441 (Fig. 4.9). This instrument used double-focusing Nier-Johnson geometry
a
mass spectrometer for secondary ion analysis with mass resolution of .~5000.
of
Transfer optics were designed that tied sensitivity the instrument to the imaged
area. The primary beam could be focused to 1-2 pm. Depth profiling with a dy-
namic range of seven decades was demonstrated for boron in silicon using beam
rastering and field aperturing (to eliminate crater edge effects). This instrument
was the first of the f series of Cameca instruments that use the same basic design.
The 4f introduced in 1985 provided scanning probe imaging as well as stigmatic
microscopic imaging.
An important development for the field was the institution of an international
conference dedicated to secondary ion mass spectrometry. Benninghoven hosted
the first conference in Muenster, Germany, in September 1977. The proceedings
were not published, but led to the formation an International Organizing Com-
of
mittee and the establishment of the Second Inte~ational Conference on Secondary
Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS 11) at Stanford University, Stanford, California, on
August 27-3 1, 1979. The proceedings of this conference were published through
the efforts of the local organizers [45]. An international conference has been held
every 2 years since. The history of the field since 1979 may be followed through
these proceedings.