Page 261 - Instant notes
P. 261
Chemical and structural effects of quantization 247
Periodicity and the periodic table
Elements in the periodic table are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, Z. The
electrons of each element (equal in number to Z) fill the atomic orbitals in order of
increasing energy, according to the rules of the Aufbau (or building-up) principle (see
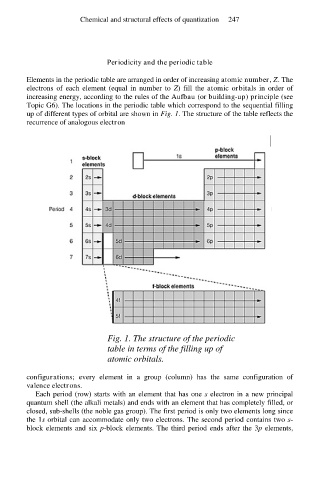
Topic G6). The locations in the periodic table which correspond to the sequential filling
up of different types of orbital are shown in Fig. 1. The structure of the table reflects the
recurrence of analogous electron
Fig. 1. The structure of the periodic
table in terms of the filling up of
atomic orbitals.
configurations; every element in a group (column) has the same configuration of
valence electrons.
Each period (row) starts with an element that has one s electron in a new principal
quantum shell (the alkali metals) and ends with an element that has completely filled, or
closed, sub-shells (the noble gas group). The first period is only two elements long since
the 1s orbital can accommodate only two electrons. The second period contains two s-
block elements and six p-block elements. The third period ends after the 3p elements,