Page 141 - Solutions Manual to accompany Electric Machinery Fundamentals
P. 141
S 2798 kVA
I base 392 A
L ,base
3V L ,base 3 4120 V
I 392 A
I ,base L ,base 226 A
3 3
Therefore, the line current of 300 A in per-unit is
I 300 A
I L 0.765 pu
,pu
L
I 392 A
L ,base
and the final per-unit current is
I pu 0.765 31.8 pu
The internal generated voltage in per-unit is
E V R I jX I
A A A S A
1
E A 0 0.1 0.765 31.8 j 0.765 31.8
1.1
E 1572 28.7 pu
A
In volts, the internal generated voltage is
E 1.572 28.7 pu 4120 V 6477 28.7 V
A
And the torque angle δ is -28.7.
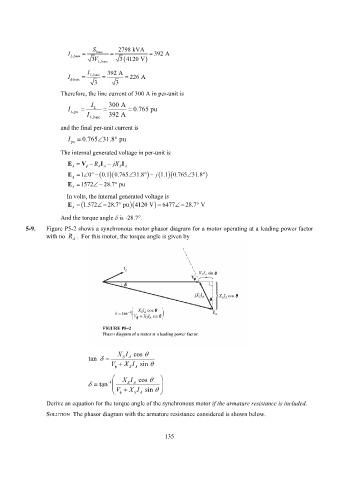
5-9. Figure P5-2 shows a synchronous motor phasor diagram for a motor operating at a leading power factor
with no R A . For this motor, the torque angle is given by
XI cos
tan SA
V X I sin
SA
XI cos
tan -1 SA
V sin
X I
SA
Derive an equation for the torque angle of the synchronous motor if the armature resistance is included.
SOLUTION The phasor diagram with the armature resistance considered is shown below.
135