Page 160 - Solutions Manual to accompany Electric Machinery Fundamentals
P. 160
P 51.3 kW
conv 171.9 N m
ind
m 2850 r/min 2 rad 1 min
1 r 60 s
(e) The rotor frequency is
f r e sf 0.05 50 Hz 2.5 Hz
6-5. A 208-V four-pole 60-Hz Y-connected wound-rotor induction motor is rated at 30 hp. Its equivalent
circuit components are
R = 0.100 R 2 = 0.070 X M = 10.0
1
X = 0.210 X 2 = 0.210
1
P mech = 500 W P misc 0 P core = 400 W
For a slip of 0.05, find
(a) The line current I L
(b) The stator copper losses P SCL
(c) The air-gap power P AG
(d) The power converted from electrical to mechanical form P conv
(e) The induced torque ind
(f) The load torque load
(g) The overall machine efficiency
(h) The motor speed in revolutions per minute and radians per second
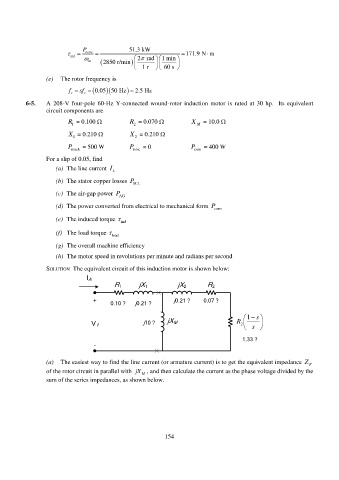
SOLUTION The equivalent circuit of this induction motor is shown below:
I A
R 1 jX 1 jX 2 R 2
+ j0.21 ? 0.07 ?
0.10 ? j0.21 ?
1 s
j10 ? jX M R
s
V ? 2
1.33 ?
-
(a) The easiest way to find the line current (or armature current) is to get the equivalent impedance Z F
of the rotor circuit in parallel with jX , and then calculate the current as the phase voltage divided by the
M
sum of the series impedances, as shown below.
154