Page 269 - Instrumentation Reference Book 3E
P. 269
Measurement techniques: direct effects 253
5x10"
L
0
>
" 20 40 60 EO 100
Temperature, 'C
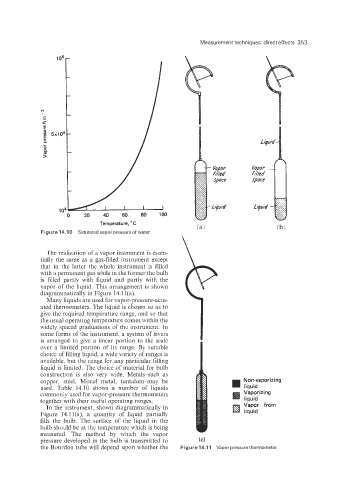
Figure 14.10 Saturated vapor pressure of water.
The realization of a vapor instrument is essen-
tially the same as a gas-filled instrument except
that in the latter the whole instrument is filled
with a permanent gas while in the former the bulb
is filled partly with liquid and partly with the
vapor of the liquid. This arrangement is shown
diagrammatically in Figure 14.1 l(a).
Many liquids are used for vapor-pressure-actu-
ated thermometers. The liquid is chosen so as to
give the required temperature range, and so that
the usual operating temperature comes within the
widely spaced graduations of the instrument. In
some forms of the instrument, a system of levers
is arranged to give a linear portion to the scale
over a limited portion of its range. By suitable
choice of filling liquid, a wide variety of ranges is
available. but the range for any particular filling
liquid is iimited. The choice of material for bulb
construction is also very wide. Metals-such as
copper, steel, Monel metal, tantalum--may be l;t,vyporizing
used. Table 14.10 shows a number of liquids
common:y used for vapor-pressure thermometers
together with their useful operating ranges.
In the instrument, shown diagrammatically in
Figure 14.11(a), a quantity of liquid partially
fills the bulb. The surface of the liquid in the
bulb should be at the temperature which is being
measured. The method by which the vapor
pressure developed in the bulb is transmitted to (C)
the Bourdon tube will depend upon whether the Figure 14.11 Vapor pressure thermometer.