Page 377 - Instrumentation Reference Book 3E
P. 377
360 Chemical analysis: electrochemical techniques
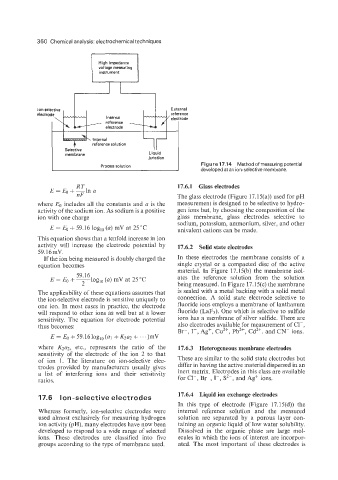
High impedance
voltage measuring
instrument
reference .
Ion-selective External
reference
electrode Internal --' electrode
electrode 'y.
L Process solution 1 developed at an ion-selective membrane.
Figure 17.14 Method of measuring potential
RT 17.6.1 Glass electrodes
E = EO + -1n a
nF The glass electrode (Figure 17.15(a)) used for pH
where EO includes all the constants and a is the measurement is designed to be selective to hydro-
activity of the sodium ion. As sodium is a positive gen ions but, by choosing the composition of the
ion with one charge glass membrane, glass electrodes selective to
sodium, potassium, ammonium, silver, and other
E = Eo + 59.16 log,, (a) mV at 25 "C univalent cations can be made.
This equation shows that a tenfold increase in ion
activity will increase the electrode potential by 17.6.2 Solid state electrodes
59.16 mV.
If the ion being measured is doubly charged the In these electrodes the membrane consists of a
equation becomes single crystal or a compacted disc of the active
material. In Figure 17.15(b) the membrane isol-
E = Eo + 59.1610g10 (a) mV at 25 "C ates the reference solution from the solution
2 being measured. In Figure 17.15(c) the membrane
The applicability of these equations assumes that is sealed with a metal backing with a solid metal
the ion-selective electrode is sensitive uniquely to connection. A solid state electrode selective to
one ion. In most cases in practice, the electrode fluoride ions employs a membrane of lanthanum
will respond to other ions as well but at a lower fluoride (LaF3). One which is selective to sulfide
sensitivity. The equation for electrode potential ions has a membrane of silver sulfide. There are
thus becomes: also electrodes available for measurement of C1-,
Br-, I-, Ag', Cu2', Pb2+, Cd2+, and CN- ions.
E =Eo+59.161ogIo(al +K2az+...)mV
where K2a2, etc., represents the ratio of the 17.6.3 Heterogeneous membrane electrodes
sensitivity of the electrode of the ion 2 to that
of ion 1. The literature on ion-selective elec- These are similar to the solid state electrodes but
trodes provided by manufacturers usually gives differ in having the active material dispersed in an
a list of interfering ions and their sensitivity inert matrix. Electrodes in this class are available
ratios. for C1-, Br-, I-, S2-, and Ag' ions.
17.6.4 Liquid ion exchange electrodes
17.6 I on -selective electrodes
In this type of electrode (Figure 17.15(d)) the
Whereas formerly, ion-selective electrodes were internal reference solution and the measured
used almost exclusively for measuring hydrogen solution are separated by a porous layer con-
ion activity (pH), many electrodes have now been taining an organic liquid of low water solubility.
developed to respond to a wide range of selected Dissolved in the organic phase are large mol-
ions. These electrodes are classified into five ecules in which the ions of interest are incorpor-
groups according to the type of membrane used. ated. The most important of these electrodes is