Page 61 - Instrumentation Reference Book 3E
P. 61
46 Measurement of viscosity
exceeded. These “plastic” materials can exhibit
various kinds of behavior above the yield stress
as shown in Figure 2.2. If the rheogram above
the yield stress is a straight line, we have what
is commonly referred to as a Bingham plastic
material.
In addition to the various possibilities shown in
Figure 2.2, there are also important “time-depend-
ent” effects exhibited by some materials; these can
be grouped under the headings ‘‘thixotropy” and
“antithixotropy.” The shearing of some mater-
~ Yield
stress ials at a constant rate can result in a substantial
/ lowering of the viscosity with time, with a gradual
return to the initial viscosity when the shearing is
stopped. This is called thixotropy. Paints are the
most obvious examples of thixotropic materials.
As the name suggests, antithixotropy involves an
Figure 2.2 Representative (7,~) rheograms. increase in viscosity with time at a constant rate-
of-shear.
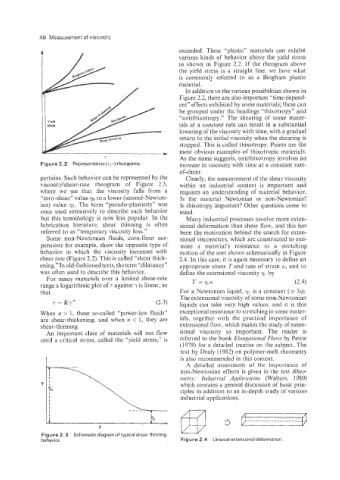
pertains. Such behavior can be represented by the Clearly, the measurement of the shear viscosity
viscositylshear-rate rheogram of Figure 2.3, within an industrial context is important and
where we see that the viscosity falls from a requires an understanding of material behavior.
“zero-shear” value 70 to a lower (second-Newton- Is the material Newtonian or non-Newtonian?
ian) value 112. The term “pseudo-plasticity” was Is thixotropy important? Other questions come to
once used extensively to describe such behavior mind.
but this terminology is now less popular. In the Many industrial processes involve more exten-
lubrication literature, shear thinning is often sional deformation than shear flow, and this has
referred to as “temporary viscosity loss.” been the motivation behind the search for exten-
Some non-Newtonian fluids, corn-flour sus- sional viscometers, which are constructed to esti-
pensions for example, show the opposite type of mate a material’s resistance to a stretching
behavior in which the viscosity increases with motion of the sort shown schematically in Figure
shear rate (Figure 2.2). This is called “shear thick- 2.4. In this case, it is again necessary to define an
ening.” In old-fashioned texts, the term “dilatancy” appropriate stress T and rate of strain 6, and to
was often used to describe this behavior. define the extensional viscosity ‘qE by
For many materials over a limited shear-rate
range a logarithmic plot of 7- against y is linear, SO T = qEfi (2.4)
that For a Newtonian liquid, 7- is a constant (= 377).
The extensional viscosity of some non-Newtonian
liquids can take very high values. and it is this
When n > 1, these so-called “power-law fluids” exceptional resistance to stretching in some mater-
are shear-thickening, and when n < 1, they are ials, together with the practical importance of
shear-thinning. extensional flow, which makes the study of exten-
An important class of materials will not flow sional viscosity so important. The reader is
until a critical stress, called the “yield stress,” is referred to the book Elongntional Floivs by Petrie
(1979) for a detailed treatise on the subject. The
text by Dealy (1952) on polymer-melt rheometry
is also recommended in this context.
A detailed assessment of the importance of
non-Newtonian effects is given in the text Rlzeo-
metry: Industrial Applications (Walters, 1980)
which contains a general discussion of basic prin-
ciples in addition to an in-depth study of various
industrial applications.
g
li I fg 0 -----__-______-___
h
7 L-- --
Figure 2.3 Schematic diagram of typical shear-thinning
behavior. Figure 2.4 Uniaxial extensional deformation