Page 56 - Instrumentation Reference Book 3E
P. 56
Flowmeter calibration methods 41
Gravimetric method Where the flow of liquid
through the meter being calibrated is diverted
into a vessel that can be weighed either continu-
ously or after a predetermined time, the weight
of the liquid is compared with the registered
reading of the flowmeter being calibrated (see
Figure 1.58).
,Tappings far use
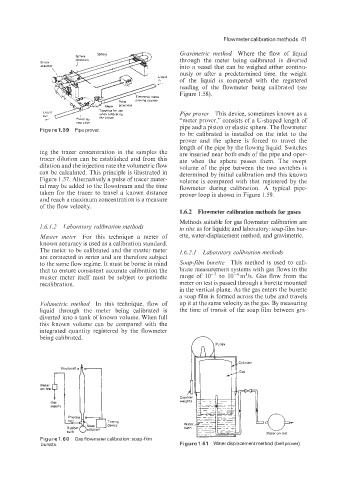
Pipe prover This device, sometimes known as a
“meter prover,’’ consists of a U-shaped length of
pas WlYe
Fig la re 1.59 Pipe prover. pipe and a piston or elastic sphere. The flowmeter
to be calibrated is installed on the inlet to the
prover and the sphere is forced to travel the
length of the pipe by the flowing liquid. Switches
ing the tracer concentration in the samples the are inserted near both ends of the pipe and oper-
tracer dilution can be established and from this ate when the sphere passes them. The swept
dilution and the injection rate the volumetric flow volume of the pipe between the two switches is
can be calculated. This principle is illustrated in determined by initial calibration and this known
Figure 1.57. Alternatively a pulse of tracer mater- volume is compared with that registered by the
ial may be added to the flowstream and the time flowmeter during calibration. A typical pipe-
taken for the tracer to travel a known distance prover loop is shown in Figure 1.59.
and reach a maximum concentration is a measure
of the flow velocity.
1.6.2 Flowmeter calibration methods for gases
Methods suitable for gas flowmeter calibration are
1.4.1.2 Laboratory calibration methods in situ: as for liquids; and laboratory: soap-film bur-
Master meter For this technique a meter of ette, water-displacement method, and gravimetric.
known accuracy is used as a calibration standard.
The meter to be calibrated and the master meter 1.6.2. I Laboratory calibration methods
are comected in series and are therefore subject
to the same flow regime. It must be borne in mind Soup-film burette This method is used to cali-
that to ensure consistent accurate calibration the brate measurement systems with gas flows in the
master meter itself must be subject to periodic range of to 10-‘m3/s. Gas flow from the
recalibration. meter on test is passed through a burette mounted
in the vertical plane. As the gas enters the burette
a soap film is formed across the tube and travels
Volumetric method In this technique, flow of up it at the same velocity as the gas. By measuring
liquid through the meter being calibrated is the time of transit of the soap film between gra-
diverted into a tank of known volume. When full
this known volume can be compared with the
integrated quantity registered by the flowmeter
being calibrated.
Meter
on tes
Timing
device
Meter on test
Figure 1 .BO Gas flowmeter calibration: soap-film
burette. Figure 1.61 Water displacement method (bell prover)