Page 57 -
P. 57
Reporting 39
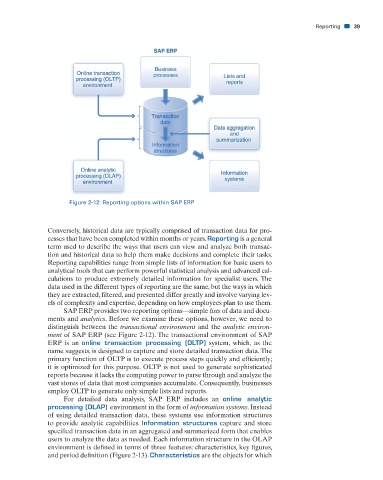
Figure 2-12: Reporting options within SAP ERP
Conversely, historical data are typically comprised of transaction data for pro-
cesses that have been completed within months or years. Reporting is a general
term used to describe the ways that users can view and analyze both transac-
tion and historical data to help them make decisions and complete their tasks.
Reporting capabilities range from simple lists of information for basic users to
analytical tools that can perform powerful statistical analysis and advanced cal-
culations to produce extremely detailed information for specialist users. The
data used in the different types of reporting are the same, but the ways in which
they are extracted, fi ltered, and presented differ greatly and involve varying lev-
els of complexity and expertise, depending on how employees plan to use them.
SAP ERP provides two reporting options—simple lists of data and docu-
ments and analytics. Before we examine these options, however, we need to
distinguish between the transactional environment and the analytic environ-
ment of SAP ERP (see Figure 2-12). The transactional environment of SAP
ERP is an online transaction processing (OLTP) system, which, as the
name suggests, is designed to capture and store detailed transaction data. The
primary function of OLTP is to execute process steps quickly and effi ciently;
it is optimized for this purpose. OLTP is not used to generate sophisticated
reports because it lacks the computing power to parse through and analyze the
vast stores of data that most companies accumulate. Consequently, businesses
employ OLTP to generate only simple lists and reports.
For detailed data analysis, SAP ERP includes an online analytic
processing (OLAP) environment in the form of information systems. Instead
of using detailed transaction data, these systems use information structures
to provide analytic capabilities. Information structures capture and store
specifi ed transaction data in an aggregated and summarized form that enables
users to analyze the data as needed. Each information structure in the OLAP
environment is defi ned in terms of three features: characteristics, key fi gures,
and period defi nition (Figure 2-13). Characteristics are the objects for which
31/01/11 1:08 PM
CH002.indd 39 31/01/11 1:08 PM
CH002.indd 39