Page 46 - Intelligent Communication Systems
P. 46
30 INTELLIGENT COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
According to this analysis, paths from node S to node G are obtained as
follows,
(1) S A C G
(2) S A B C G
(3) S A B G
(4) S B C G
(5) S B G
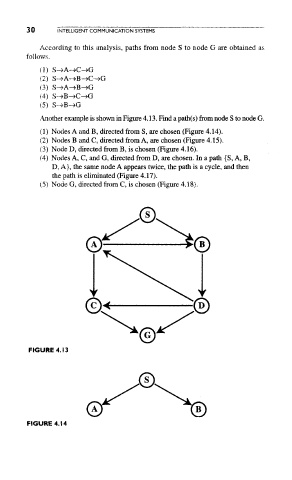
Another example is shown in Figure 4.13. Find a path(s) from node S to node G.
(1) Nodes A and B, directed from S, are chosen (Figure 4.14).
(2) Nodes B and C, directed from A, are chosen (Figure 4.15).
(3) Node D, directed from B, is chosen (Figure 4.16).
(4) Nodes A, C, and G, directed from D, are chosen. In a path {S, A, B,
D, A}, the same node A appears twice, the path is a cycle, and then
the path is eliminated (Figure 4.17).
(5) Node G, directed from C, is chosen (Figure 4.18).
FIGURE 4.13
FIGURE 4.14