Page 47 - Intelligent Communication Systems
P. 47
CHAPTER 4 /ADVANCES IN COMMUNICATION NETWORKS 3 i
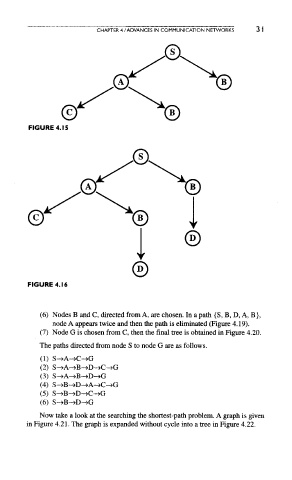
FIGURE 4.15
FIGURE 4.16
(6) Nodes B and C, directed from A, are chosen. In a path {S, B, D, A, B},
node A appears twice and then the path is eliminated (Figure 4.19).
(7) Node G is chosen from C, then the final tree is obtained in Figure 4.20.
The paths directed from node S to node G are as follows.
(1) S A C G
(2) S A B D C G
(3) S A B D G
(4) S B D A C G
(5) S B D C G
(6) S B D G
Now take a look at the searching the shortest-path problem. A graph is given
in Figure 4.21. The graph is expanded without cycle into a tree in Figure 4.22.