Page 217 - Intelligent Digital Oil And Gas Fields
P. 217
Workflow Automation and Intelligent Control 171
45,000 100
Flow meter, MSCF/d VFM, MSCF/d Well test, MSCF/d NonStac VFM, MSCF/d Chk size
90
40,000
80
35,000
70
Gas flow rates. MSCF/d 25,000 48/64" 50
30,000
60
20,000
40
15,000
24/64" 32/64" 30
10,000 20
5000 10
0 0
12 34567 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
Time, days
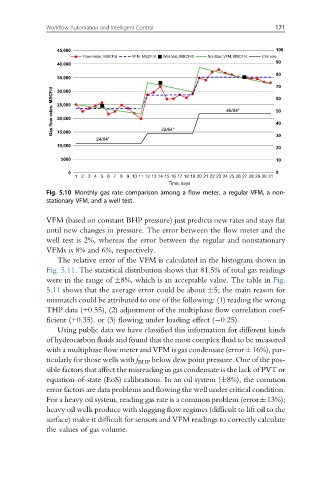
Fig. 5.10 Monthly gas rate comparison among a flow meter, a regular VFM, a non-
stationary VFM, and a well test.
VFM (based on constant BHP pressure) just predicts new rates and stays flat
until new changes in pressure. The error between the flow meter and the
well test is 2%, whereas the error between the regular and nonstationary
VFMs is 8% and 6%, respectively.
The relative error of the VFM is calculated in the histogram shown in
Fig. 5.11. The statistical distribution shows that 81.5% of total gas readings
were in the range of 8%, which is an acceptable value. The table in Fig.
5.11 shows that the average error could be about 5; the main reason for
mismatch could be attributed to one of the following: (1) reading the wrong
THP data (+0.55), (2) adjustment of the multiphase flow correlation coef-
ficient (+0.35), or (3) flowing under loading effect ( 0.25).
Using public data we have classified this information for different kinds
of hydrocarbon fluids and found that the most complex fluid to be measured
with a multiphase flow meter and VFM is gas condensate (error 16%), par-
ticularly for those wells with f BHP below dew point pressure. One of the pos-
sible factors that affect the misreading in gas condensate is the lack of PVT or
equation-of-state (EoS) calibrations. In an oil system ( 8%), the common
error factors are data problems and flowing the well under critical condition.
For a heavy oil system, reading gas rate is a common problem (error 13%);
heavy oil wells produce with slugging flow regimes (difficult to lift oil to the
surface) make it difficult for sensors and VFM readings to correctly calculate
the values of gas volume.