Page 215 - Intelligent Digital Oil And Gas Fields
P. 215
Workflow Automation and Intelligent Control 169
Choke model (surface)
Calculate oil, water, gas rates Test
THP Operating point
IPR Model Chk 48/64"
Chk 32/64"
Estimate fBHP
Test
fBHP
Operating point
VLP model
Pressure losses
Fluid rates
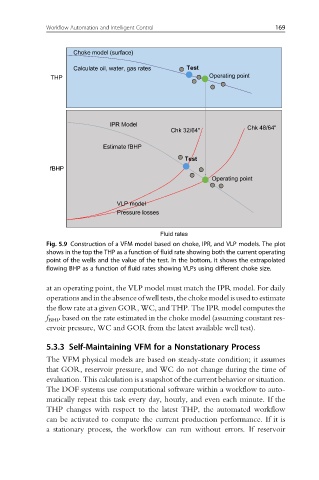
Fig. 5.9 Construction of a VFM model based on choke, IPR, and VLP models. The plot
shows in the top the THP as a function of fluid rate showing both the current operating
point of the wells and the value of the test. In the bottom, it shows the extrapolated
flowing BHP as a function of fluid rates showing VLPs using different choke size.
at an operating point, the VLP model must match the IPR model. For daily
operations andin the absenceof well tests, the choke model isusedto estimate
the flow rate at a given GOR, WC, and THP. The IPR model computes the
f BHP based on the rate estimated in the choke model (assuming constant res-
ervoir pressure, WC and GOR from the latest available well test).
5.3.3 Self-Maintaining VFM for a Nonstationary Process
The VFM physical models are based on steady-state condition; it assumes
that GOR, reservoir pressure, and WC do not change during the time of
evaluation. This calculation is a snapshot of the current behavior or situation.
The DOF systems use computational software within a workflow to auto-
matically repeat this task every day, hourly, and even each minute. If the
THP changes with respect to the latest THP, the automated workflow
can be activated to compute the current production performance. If it is
a stationary process, the workflow can run without errors. If reservoir