Page 205 - Intermediate Statistics for Dummies
P. 205
16_045206 ch10.qxd 2/1/07 10:14 AM Page 184
184
Part III: Comparing Many Means with ANOVA
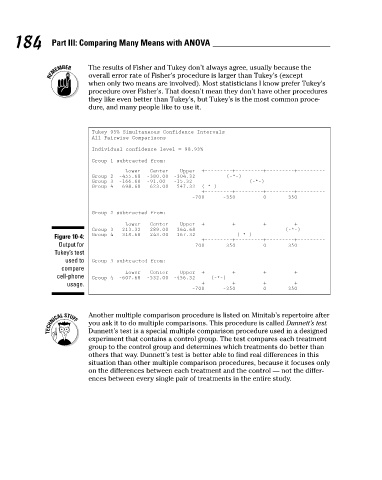
The results of Fisher and Tukey don’t always agree, usually because the
overall error rate of Fisher’s procedure is larger than Tukey’s (except
when only two means are involved). Most statisticians I know prefer Tukey’s
procedure over Fisher’s. That doesn’t mean they don’t have other procedures
they like even better than Tukey’s, but Tukey’s is the most common proce-
dure, and many people like to use it.
Tukey 95% Simultaneous Confidence Intervals
All Pairwise Comparisons
Individual confidence level = 98.93%
Group 1 subtracted from:
Lower
Center
Upper +–––––––––+–––––––––+–––––––––+–––––––––
(–*–)
Group 2 –455.68 –380.00 –304.32
(–*–)
Group 3 –166.68 –91.00 –15.32
Group 4 –698.68 –623.00 –547.32 (–*–)
+–––––––––+–––––––––+–––––––––+–––––––––
Group 2 subtracted from: –700 –350 0 350
Lower Center Upper +–––––––––+–––––––––+–––––––––+–––––––––
Group 3 213.32 289.00 364.68 (–*-)
Figure 10-4: Group 4 –318.68 –243.00 –167.32 (–*–)
+–––––––––+–––––––––+–––––––––+–––––––––
Output for –700 –350 0 350
Tukey’s test
used to Group 3 subtracted from:
compare
Lower Center Upper +–––––––––+–––––––––+–––––––––+–––––––––
cell-phone Group 4 –607.68 –532.00 –456.32 (–*–)
usage. +–––––––––+–––––––––+–––––––––+–––––––––
–700 –350 0 350
Another multiple comparison procedure is listed on Minitab’s repertoire after
you ask it to do multiple comparisons. This procedure is called Dunnett’s test.
Dunnett’s test is a special multiple comparison procedure used in a designed
experiment that contains a control group. The test compares each treatment
group to the control group and determines which treatments do better than
others that way. Dunnett’s test is better able to find real differences in this
situation than other multiple comparison procedures, because it focuses only
on the differences between each treatment and the control — not the differ-
ences between every single pair of treatments in the entire study.