Page 228 - Intro Predictive Maintenance
P. 228
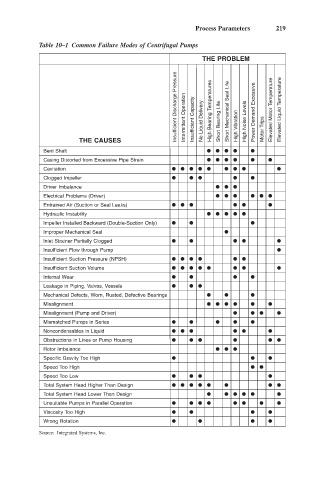
Process Parameters 219
Table 10–1 Common Failure Modes of Centrifugal Pumps
THE PROBLEM
Insufficient Discharge Pressure Intermittent Operation Insufficient Capacity No Liquid Delivery High Bearing Temperatures Short Bearing Life Short Mechanical Seal Life High Noise Levels Power Demand Excessive Elevated Motor Temperature Elevated Liquid Temperature
THE CAUSES High Vibration Motor Trips
Bent Shaft
Casing Distorted from Excessive Pipe Strain
Cavitation
Clogged Impeller
Driver Imbalance
Electrical Problems (Driver)
Entrained Air (Suction or Seal Leaks)
Hydraulic Instability
Impeller Installed Backward (Double-Suction Only)
Improper Mechanical Seal
Inlet Strainer Partially Clogged
Insufficient Flow through Pump
Insufficient Suction Pressure (NPSH)
Insufficient Suction Volume
Internal Wear
Leakage in Piping, Valves, Vessels
Mechanical Defects, Worn, Rusted, Defective Bearings
Misalignment
Misalignment (Pump and Driver)
Mismatched Pumps in Series
Noncondensables in Liquid
Obstructions in Lines or Pump Housing
Rotor Imbalance
Specific Gravity Too High
Speed Too High
Speed Too Low
Total System Head Higher Than Design
Total System Head Lower Than Design
Unsuitable Pumps in Parallel Operation
Viscosity Too High
Wrong Rotation
Source: Integrated Systems, Inc.