Page 232 - Intro Predictive Maintenance
P. 232
Process Parameters 223
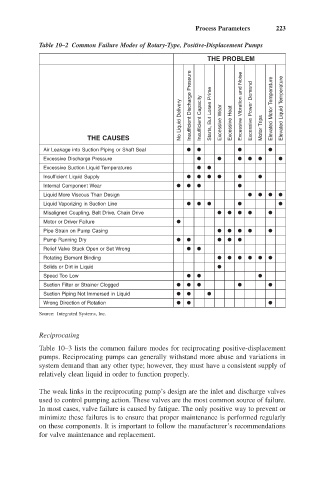
Table 10–2 Common Failure Modes of Rotary-Type, Positive-Displacement Pumps
THE PROBLEM
No Liquid Delivery Insufficient Discharge Pressure Insufficient Capacity Starts, But Loses Prime Excessive Wear Excessive Heat Excessive Vibration and Noise Excessive Power Demand Motor Trips Elevated Motor Temperature Elevated Liquid Temperature
THE CAUSES
Air Leakage into Suction Piping or Shaft Seal
Excessive Discharge Pressure
Excessive Suction Liquid Temperatures
Insufficient Liquid Supply
Internal Component Wear
Liquid More Viscous Than Design
Liquid Vaporizing in Suction Line
Misaligned Coupling, Belt Drive, Chain Drive
Motor or Driver Failure
Pipe Strain on Pump Casing
Pump Running Dry
Relief Valve Stuck Open or Set Wrong
Rotating Element Binding
Solids or Dirt in Liquid
Speed Too Low
Suction Filter or Strainer Clogged
Suction Piping Not Immersed in Liquid
Wrong Direction of Rotation
Source: Integrated Systems, Inc.
Reciprocating
Table 10–3 lists the common failure modes for reciprocating positive-displacement
pumps. Reciprocating pumps can generally withstand more abuse and variations in
system demand than any other type; however, they must have a consistent supply of
relatively clean liquid in order to function properly.
The weak links in the reciprocating pump’s design are the inlet and discharge valves
used to control pumping action. These valves are the most common source of failure.
In most cases, valve failure is caused by fatigue. The only positive way to prevent or
minimize these failures is to ensure that proper maintenance is performed regularly
on these components. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations
for valve maintenance and replacement.