Page 261 - Intro Predictive Maintenance
P. 261
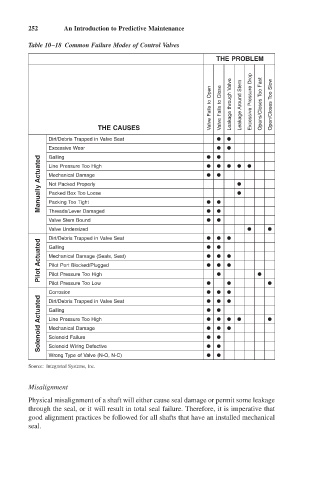
252 An Introduction to Predictive Maintenance
Table 10–18 Common Failure Modes of Control Valves
THE PROBLEM
Valve Fails to Open Valve Fails to Close Leakage through Valve Leakage Around Stem Excessive Pressure Drop Opens/Closes Too Fast Open/Closes Too Slow
THE CAUSES
Dirt/Debris Trapped in Valve Seat
Excessive Wear
Galling
Manually Actuated Line Pressure Too High
Mechanical Damage
Not Packed Properly
Packed Box Too Loose
Packing Too Tight
Threads/Lever Damaged
Valve Stem Bound
Valve Undersized
Dirt/Debris Trapped in Valve Seat
Pilot Actuated Mechanical Damage (Seals, Seat)
Galling
Pilot Port Blocked/Plugged
Pilot Pressure Too High
Pilot Pressure Too Low
Corrosion
Solenoid Actuated Galling
Dirt/Debris Trapped in Valve Seat
Line Pressure Too High
Mechanical Damage
Solenoid Failure
Solenoid Wiring Defective
Wrong Type of Valve (N-O, N-C)
Source: Integrated Systems, Inc.
Misalignment
Physical misalignment of a shaft will either cause seal damage or permit some leakage
through the seal, or it will result in total seal failure. Therefore, it is imperative that
good alignment practices be followed for all shafts that have an installed mechanical
seal.