Page 318 - Intro Predictive Maintenance
P. 318
Failure-Mode Analysis 309
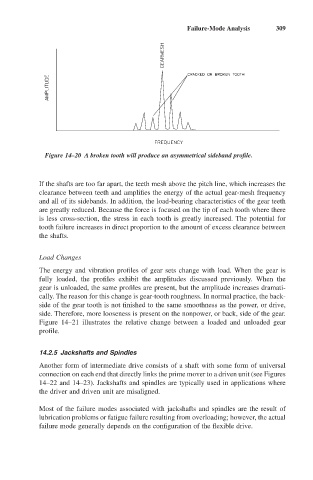
Figure 14–20 A broken tooth will produce an asymmetrical sideband profile.
If the shafts are too far apart, the teeth mesh above the pitch line, which increases the
clearance between teeth and amplifies the energy of the actual gear-mesh frequency
and all of its sidebands. In addition, the load-bearing characteristics of the gear teeth
are greatly reduced. Because the force is focused on the tip of each tooth where there
is less cross-section, the stress in each tooth is greatly increased. The potential for
tooth failure increases in direct proportion to the amount of excess clearance between
the shafts.
Load Changes
The energy and vibration profiles of gear sets change with load. When the gear is
fully loaded, the profiles exhibit the amplitudes discussed previously. When the
gear is unloaded, the same profiles are present, but the amplitude increases dramati-
cally. The reason for this change is gear-tooth roughness. In normal practice, the back-
side of the gear tooth is not finished to the same smoothness as the power, or drive,
side. Therefore, more looseness is present on the nonpower, or back, side of the gear.
Figure 14–21 illustrates the relative change between a loaded and unloaded gear
profile.
14.2.5 Jackshafts and Spindles
Another form of intermediate drive consists of a shaft with some form of universal
connection on each end that directly links the prime mover to a driven unit (see Figures
14–22 and 14–23). Jackshafts and spindles are typically used in applications where
the driver and driven unit are misaligned.
Most of the failure modes associated with jackshafts and spindles are the result of
lubrication problems or fatigue failure resulting from overloading; however, the actual
failure mode generally depends on the configuration of the flexible drive.