Page 247 - Introduction to AI Robotics
P. 247
230
6 Common Sensing Techniques for Reactive Robots
red green blue white
b.
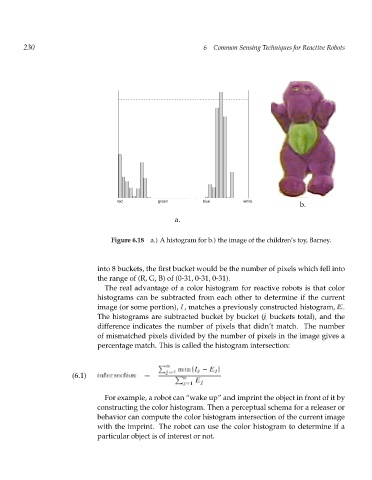
a.
Figure 6.18 a.) A histogram for b.) the image of the children’s toy, Barney.
into 8 buckets, the first bucket would be the number of pixels which fell into
the range of (R, G, B) of (0-31, 0-31, 0-31).
The real advantage of a color histogram for reactive robots is that color
histograms can be subtracted from each other to determine if the current
image (or some portion), I, matches a previously constructed histogram, E.
The histograms are subtracted bucket by bucket (j buckets total), and the
difference indicates the number of pixels that didn’t match. The number
of mismatched pixels divided by the number of pixels in the image gives a
percentage match. This is called the histogram intersection:
P n E j )
j=1 min (I j
(6.1) intersection = P n
j=1 E j
For example, a robot can “wake up” and imprint the object in front of it by
constructing the color histogram. Then a perceptual schema for a releaser or
behavior can compute the color histogram intersection of the current image
with the imprint. The robot can use the color histogram to determine if a
particular object is of interest or not.