Page 262 - Introduction to AI Robotics
P. 262
245
6.8 Case Study: Hors d’Oeuvres, Anyone?
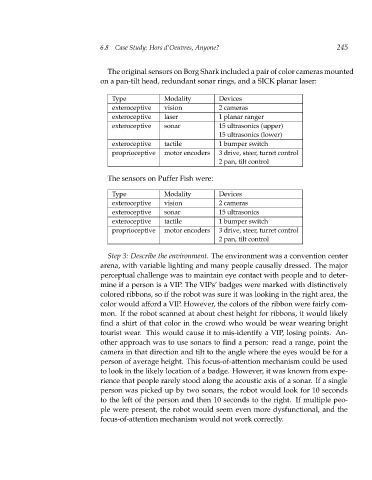
The original sensors on Borg Shark included a pair of color cameras mounted
on a pan-tilt head, redundant sonar rings, and a SICK planar laser:
Type Modality Devices
exteroceptive vision 2 cameras
exteroceptive laser 1planar ranger
exteroceptive sonar 15 ultrasonics (upper)
15 ultrasonics (lower)
exteroceptive tactile 1 bumper switch
proprioceptive motor encoders 3 drive, steer, turret control
2 pan, tilt control
The sensors on Puffer Fish were:
Type Modality Devices
exteroceptive vision 2 cameras
exteroceptive sonar 15 ultrasonics
exteroceptive tactile 1 bumper switch
proprioceptive motor encoders 3 drive, steer, turret control
2 pan, tilt control
Step 3: Describe the environment. The environment was a convention center
arena, with variable lighting and many people causally dressed. The major
perceptual challenge was to maintain eye contact with people and to deter-
mine if a person is a VIP. The VIPs’ badges were marked with distinctively
colored ribbons, so if the robot was sure it was looking in the right area, the
color would afford a VIP. However, the colors of the ribbon were fairly com-
mon. If the robot scanned at about chest height for ribbons, it would likely
find a shirt of that color in the crowd who would be wear wearing bright
tourist wear. This would cause it to mis-identify a VIP, losing points. An-
other approach was to use sonars to find a person: read a range, point the
camera in that direction and tilt to the angle where the eyes would be for a
person of average height. This focus-of-attention mechanism could be used
to look in the likely location of a badge. However, it was known from expe-
rience that people rarely stood along the acoustic axis of a sonar. If a single
person was picked up by two sonars, the robot would look for 10 seconds
to the left of the person and then 10 seconds to the right. If multiple peo-
ple were present, the robot would seem even more dysfunctional, and the
focus-of-attention mechanism would not work correctly.