Page 106 - Introduction to Autonomous Mobile Robots
P. 106
91
Perception
and those beyond its control. For example, signals emitted by other nearby robots, or sim-
ilar sensors on the same robot, may influence the resulting measurements. Examples of
active sensors include wheel quadrature encoders, ultrasonic sensors, and laser rangefind-
ers.
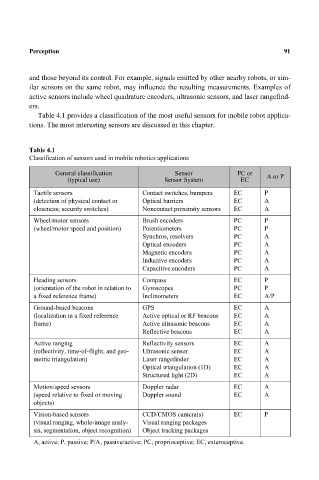
Table 4.1 provides a classification of the most useful sensors for mobile robot applica-
tions. The most interesting sensors are discussed in this chapter.
Table 4.1
Classification of sensors used in mobile robotics applications
General classification Sensor PC or A or P
(typical use) Sensor System EC
Tactile sensors Contact switches, bumpers EC P
(detection of physical contact or Optical barriers EC A
closeness; security switches) Noncontact proximity sensors EC A
Wheel/motor sensors Brush encoders PC P
(wheel/motor speed and position) Potentiometers PC P
Synchros, resolvers PC A
Optical encoders PC A
Magnetic encoders PC A
Inductive encoders PC A
Capacitive encoders PC A
Heading sensors Compass EC P
(orientation of the robot in relation to Gyroscopes PC P
a fixed reference frame) Inclinometers EC A/P
Ground-based beacons GPS EC A
(localization in a fixed reference Active optical or RF beacons EC A
frame) Active ultrasonic beacons EC A
Reflective beacons EC A
Active ranging Reflectivity sensors EC A
(reflectivity, time-of-flight, and geo- Ultrasonic sensor EC A
metric triangulation) Laser rangefinder EC A
Optical triangulation (1D) EC A
Structured light (2D) EC A
Motion/speed sensors Doppler radar EC A
(speed relative to fixed or moving Doppler sound EC A
objects)
Vision-based sensors CCD/CMOS camera(s) EC P
(visual ranging, whole-image analy- Visual ranging packages
sis, segmentation, object recognition) Object tracking packages
A, active; P, passive; P/A, passive/active; PC, proprioceptive; EC, exteroceptive.