Page 266 - Introduction to Autonomous Mobile Robots
P. 266
Mobile Robot Localization
Map 251
Map Building and Maintenance
Refine Feature Add New Remove Offensive
Encoder Parameters Features Features
increase credibility extend map decrease credibility
position
Prediction of Mea- estimate Estimation (fusion)
surement and Posi- using confirmed
tion (odometry) map matched predic-
predicted feature observations YES and observations YES observations unobserved
unexpected
tions
predictions
Matching NO Unexpected NO
Observation?
raw sensor data or
extracted features
Perception on-board sensors
Observation
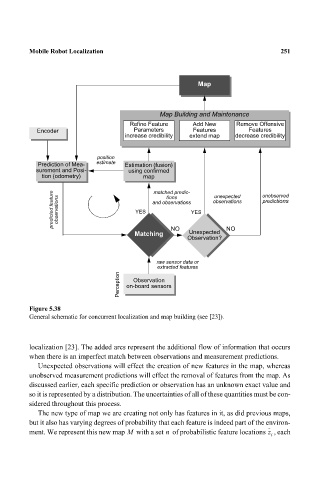
Figure 5.38
General schematic for concurrent localization and map building (see [23]).
localization [23]. The added arcs represent the additional flow of information that occurs
when there is an imperfect match between observations and measurement predictions.
Unexpected observations will effect the creation of new features in the map, whereas
unobserved measurement predictions will effect the removal of features from the map. As
discussed earlier, each specific prediction or observation has an unknown exact value and
so it is represented by a distribution. The uncertainties of all of these quantities must be con-
sidered throughout this process.
The new type of map we are creating not only has features in it, as did previous maps,
but it also has varying degrees of probability that each feature is indeed part of the environ-
ˆ
z
n
ment. We represent this new map M with a set of probabilistic feature locations , each
t