Page 40 - Introduction to Colloid and Surface Chemistry
P. 40
Kinetic properties 31
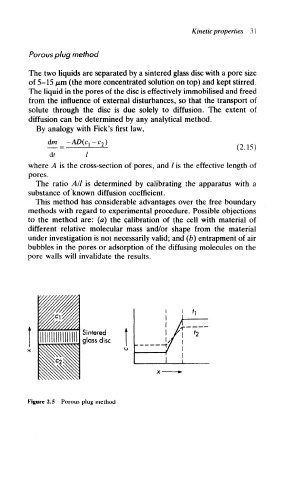
Porous plug method
The two liquids are separated by a sintered glass disc with a pore size
of 5-15 fjLm (the more concentrated solution on top) and kept stirred.
The liquid in the pores of the disc is effectively immobilised and freed
from the influence of external disturbances, so that the transport of
solute through the disc is due solely to diffusion. The extent of
diffusion can be determined by any analytical method.
By analogy with Pick's first law,
dm _ -AD(c { -c 2 )
(2.15)
d/ /
where A is the cross-section of pores, and / is the effective length of
pores.
The ratio All is determined by calibrating the apparatus with a
substance of known diffusion coefficient.
This method has considerable advantages over the free boundary
methods with regard to experimental procedure. Possible objections
to the method are: (a) the calibration of the cell with material of
different relative molecular mass and/or shape from the material
under investigation is not necessarily valid; and (b) entrapment of air
bubbles in the pores or adsorption of the diffusing molecules on the
pore walls will invalidate the results.
Sintered
glass disc
Figure 2.5 Porous plug method