Page 291 - Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics
P. 291
P2: IWV
P1: IWV/KCX
0 521 85326 5
15:41
May 11, 2005
0521853265c09
CB908/Date
270
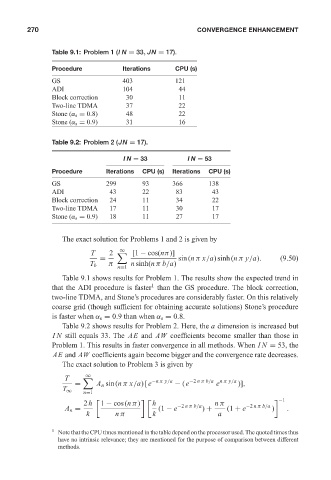
Table 9.1: Problem 1 (IN = 33, JN = 17). CONVERGENCE ENHANCEMENT
Procedure Iterations CPU (s)
GS 403 121
ADI 104 44
Block correction 30 11
Two-line TDMA 37 22
Stone (α s = 0.8) 48 22
Stone (α s = 0.9) 31 16
Table 9.2: Problem 2 (JN = 17).
IN = 33 IN = 53
Procedure Iterations CPU (s) Iterations CPU (s)
GS 299 93 366 138
ADI 43 22 83 43
Block correction 24 11 34 22
Two-line TDMA 17 11 30 17
Stone (α s = 0.9) 18 11 27 17
The exact solution for Problems 1 and 2 is given by
∞
T 2 [1 − cos(nπ)]
= sin(n π x/a)sinh(n π y/a). (9.50)
π n sinh(n π b/a)
T b
n=1
Table 9.1 shows results for Problem 1. The results show the expected trend in
1
that the ADI procedure is faster than the GS procedure. The block correction,
two-line TDMA, and Stone’s procedures are considerably faster. On this relatively
coarse grid (though sufficient for obtaining accurate solutions) Stone’s procedure
is faster when α s = 0.9 than when α s = 0.8.
Table 9.2 shows results for Problem 2. Here, the a dimension is increased but
IN still equals 33. The AE and AW coefficients become smaller than those in
Problem 1. This results in faster convergence in all methods. When IN = 53, the
AE and AW coefficients again become bigger and the convergence rate decreases.
The exact solution to Problem 3 is given by
∞
T −n π y/a −2 n π b/a n π y/a
= A n sin(n π x/a)[e − (e e )],
T ∞
n=1
2h 1 − cos(n π) h −2 n π b/a n π −2 n π b/a −1
A n = (1 − e ) + (1 + e ) .
k n π k a
1 Note that the CPU times mentioned in the table depend on the processor used. The quoted times thus
have no intrinsic relevance; they are mentioned for the purpose of comparison between different
methods.