Page 187 - Introduction to Electronic Commerce and Social Commerce
P. 187
170 6 Mobile Commerce and the Internet of Things
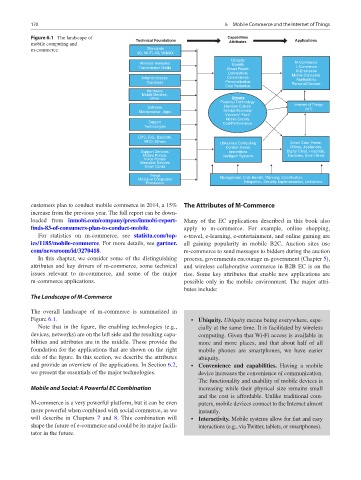
Figure 6.1 The landscape of Technical Foundations Capabilities Applications
mobile computing and Attributes
m-commerce Standards
3G, Wi-Fi, 4G, WiMAX
Ubiquity
Wireless Networks Mobility M-Commerce
Transmission Media Broad Reach L-Commerce
Connectivity M-Enterprise
Internet Access Convenience Mobile Consumer
Applications
Standards Personalization Personal Devices
Cost Reduction
Hardware
Mobile Devices,
Other Drivers
Powerful Technology Internet of Things
Software Handset Culture (IoT)
Microbrowser, Apps Service Economy
Vendors* Push
Mobile Society
Support Cost/Performance
Technologies
GPS, GIS, Barcode,
RFID, Others Ubiquitous Computing Smart Cars, Home,
Context-Aware Offices, Appliances,
Support Services Innovations Digital Cities, Hospitals,
Mobile Portals Intelligent Systems Factories, Smart Grids
Voice Portals
Wearable Devices
Smart Carda
Things
Miniature Computers Management: Cost-Benefit, Planning, Coordination,
Processors Integration, Security Implementation, Limitations
customers plan to conduct mobile commerce in 2014, a 15% The Attributes of M-Commerce
increase from the previous year. The full report can be down-
loaded from inmobi.com/company/press/inmobi-report- Many of the EC applications described in this book also
finds-83-of-consumers-plan-to-conduct- mobile. apply to m-commerce. For example, online shopping,
For statistics on m-commerce, see statista.com/top- e-travel, e-learning, e-entertainment, and online gaming are
ics/1185/mobile-commerce. For more details, see gartner. all gaining popularity in mobile B2C. Auction sites use
com/newsroom/id/3270418. m-commerce to send messages to bidders during the auction
In this chapter, we consider some of the distinguishing process, governments encourage m-government (Chapter 5),
attributes and key drivers of m-commerce, some technical and wireless collaborative commerce in B2B EC is on the
issues relevant to m-commerce, and some of the major rise. Some key attributes that enable new applications are
m-commerce applications. possible only in the mobile environment. The major attri-
butes include:
The Landscape of M-Commerce
The overall landscape of m-commerce is summarized in
Figure 6.1. • Ubiquity. Ubiquity means being everywhere, espe-
Note that in the figure, the enabling technologies (e.g., cially at the same time. It is facilitated by wireless
devices, networks) are on the left side and the resulting capa- computing. Given that Wi-Fi access is available in
bilities and attributes are in the middle. These provide the more and more places, and that about half of all
foundation for the applications that are shown on the right mobile phones are smartphones, we have easier
side of the figure. In this section, we describe the attributes ubiquity.
and provide an overview of the applications. In Section 6.2, • Convenience and capabilities. Having a mobile
we present the essentials of the major technologies. device increases the convenience of communication.
The functionality and usability of mobile devices is
Mobile and Social: A Powerful EC Combination increasing while their physical size remains small
and the cost is affordable. Unlike traditional com-
M-commerce is a very powerful platform, but it can be even puters, mobile devices connect to the Internet almost
more powerful when combined with social commerce, as we instantly.
will describe in Chapters 7 and 8. This combination will • Interactivity. Mobile systems allow for fast and easy
shape the future of e-commerce and could be its major facili- interactions (e.g., via Twitter, tablets, or smartphones).
tator in the future.