Page 188 - Introduction to Electronic Commerce and Social Commerce
P. 188
6.1 Mobile Commerce: Concepts, Landscape, Attributes, Drivers, Applications, and Benefits 171
• Personalization. Mobile devices are personal devices. • Banking and financial services—Section 6.3.
While several people may share the same PC, a spe- • Mobile enterprise applications—Section 6.4.
cific mobile device is usually used by one person. • Consumer services (including shopping) and enter-
• Localization. Knowing where a user is physically tainment—Section 6.5.
located in real time provides an opportunity to offer • Ubiquitous computing—Section 6.6.
him or her relevant mobile advertisements, cou- • Internet of Things (IoT) applications are covered in
pons, or other services. Such services are known as Section 6.7.
location-based m-commerce. • Emerging applications: Wearables, Google Glass,
smart grid, and driverless cars—Section 6.8.
• Mobile shopping is covered in Chapter 7.
• Mobile marketing and advertising are covered in
Chapter 9.
• Mobile payment is introduced in Chapter 11.
Mobile vendors differentiate themselves from wireline
vendors by offering unique services based on the above attri-
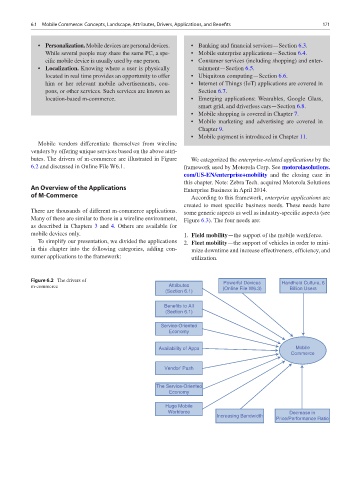
butes. The drivers of m-commerce are illustrated in Figure We categorized the enterprise-related applications by the
6.2 and discussed in Online File W6.1. framework used by Motorola Corp. See motorolasolutions.
com/US-EN/enterprise+mobility and the closing case in
this chapter. Note: Zebra Tech. acquired Motorola Solutions
An Overview of the Applications Enterprise Business in April 2014.
of M-Commerce According to this framework, enterprise applications are
created to meet specific business needs. These needs have
There are thousands of different m-commerce applications. some generic aspects as well as industry-specific aspects (see
Many of these are similar to those in a wireline environment, Figure 6.3). The four needs are:
as described in Chapters 3 and 4. Others are available for
mobile devices only. 1. Field mobility—the support of the mobile workforce.
To simplify our presentation, we divided the applications 2. Fleet mobility—the support of vehicles in order to mini-
in this chapter into the following categories, adding con- mize downtime and increase effectiveness, efficiency, and
sumer applications to the framework: utilization.
Figure 6.2 The drivers of Powerful Devices Handheld Culture, 6
m-commerce Attributes (Online File W6.3) Billion Users
(Section 6.1)
Benefits to All
(Section 6.1)
Service-Oriented
Economy
Availability of Apps Mobile
Commerce
Vendor’ Push
The Service-Oriented
Economy
Huge Mobile
Workforce Decrease in
Increasing Bandwidth
Price/Performance Ratio