Page 78 - Introduction to Electronic Commerce and Social Commerce
P. 78
56 2 E-Commerce: Mechanisms, Platforms, and Tools
Definitions and Major Concepts models and processes used by the crowd to execute the task.
These elements are connected by features related to the tasks
The term crowd refers to a large group of people such as a and the crowd (such as the psychology of the crowd), the tech-
group of consumers, employees of a corporation, or mem- nologies used (such as idea generation and voting), and imple-
bers of a social network who offer expertise. mentation issues such as incentives paid to the participants.
AR is developed into apps for mobile devices to blend
digital components into real worlds. The Process of Crowdsourcing
Crowdsourcing utilizes crowds to collectively execute
tasks such as solving problems, innovating, or getting large Crowdsourcing can be viewed as a collective problem-
projects completed by dividing the work among many peo- solving or work-sharing process, and usually is conducted as
ple. The term was coined by Jeff Howe in June 2006 (Howe a Web-based activity. In a typical use of crowdsourcing,
2008). In the crowdsourcing process, the initiator recruits a problems are broadcasted either to a known crowd (e.g.,
crowd (e.g., customers) to create content, a cumbersome task employees or business partners) or to an unknown group of
(e.g., translating Wikipedia articles), or in research and participants (e.g., expert problem solvers or consumers). The
development. This is based on the idea that two heads are communication usually starts as an open call for solutions or
better than one. The collective intelligence of large groups is ideas (see first step in Figure 2.5). The members of the crowd
assumed to be able to solve complex problems at low cost are organized as an online community, and the members sub-
(Zeref 2015; Brabham 2013). mit individual work (e.g., solutions). The crowd may also
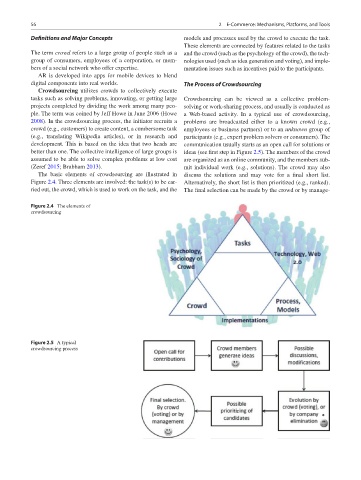
The basic elements of crowdsourcing are illustrated in discuss the solutions and may vote for a final short list.
Figure 2.4. Three elements are involved: the task(s) to be car- Alternatively, the short list is then prioritized (e.g., ranked).
ried out, the crowd, which is used to work on the task, and the The final selection can be made by the crowd or by manage-
Figure 2.4 The elements of
crowdsourcing
Figure 2.5 A typical
crowdsourcing process