Page 102 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 102
2.4. Fourier Transform Processing
Reference
object
Correlation
peak
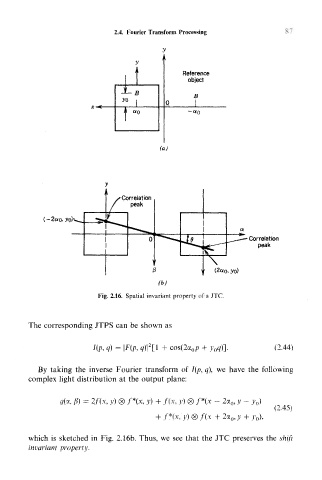
Fig. 2.16. Spatial invariant property of a JTC.
The corresponding JTPS can be shown as
2
I(p, q) = \F(p, q)\ [l + cos(2a 0p + y 0q)]. (2.44)
By taking the inverse Fourier transform of /(p, q), we have the following
complex light distribution at the output plane:
2/(x, y) (g) /*(x, >') + /(x, v) ® /*(x - 2a 0, y -
(2.45)
+ /*(x, y)(x)/(x+2a 0 ,y +
which is sketched in Fig. 2.16b. Thus, we see that the JTC preserves the shift
invariant property.